Jacob Jordaens
1593, Antwerp – 1678, Antwerp, Belgium
♦ The painter's family ♦
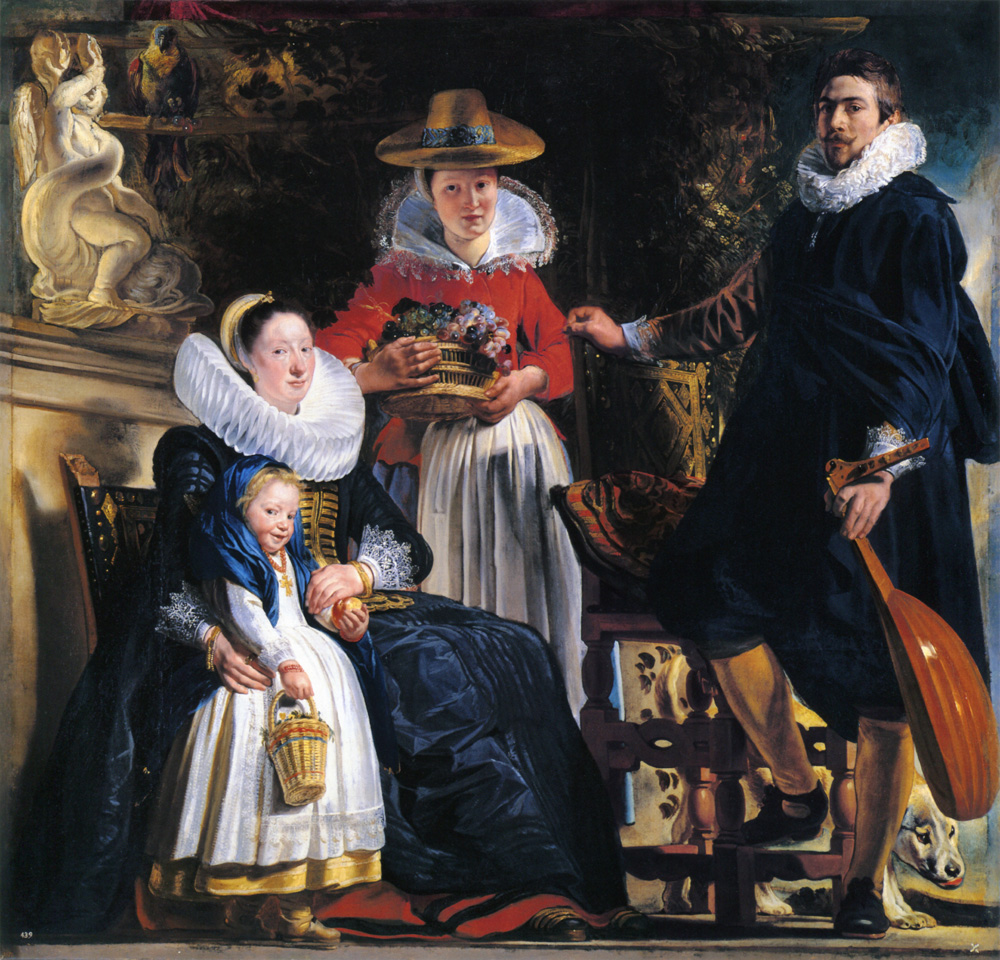
In this painting, Jordaens depicts himself surrounded by his household members.
The painter himself stands on the right, with one foot casually resting on the crossbar of a chair, while his hand seeks support on the backrest.
With his left hand, he holds the neck of the lute.
His wife, elegantly dressed and wearing a large collar, is depicted on the left. She is sitting on a low chair and her right arm loosely embraces a girl.
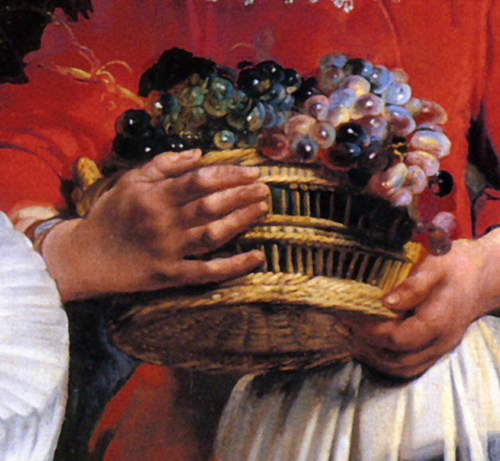
The child is holding a basket of flowers in one hand and an apple in the other.
In the middle between the spouses stands an older girl. Although she is also depicted frontally, she is the only one of the group who is not looking “straight into the lens”. This older girl is generally considered to be the housemaid.
♦ Diagnosis
Main symptoms:
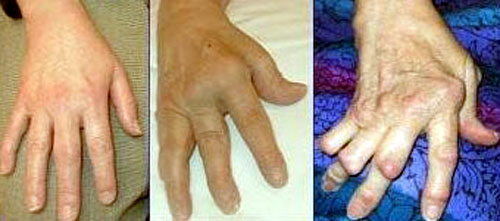
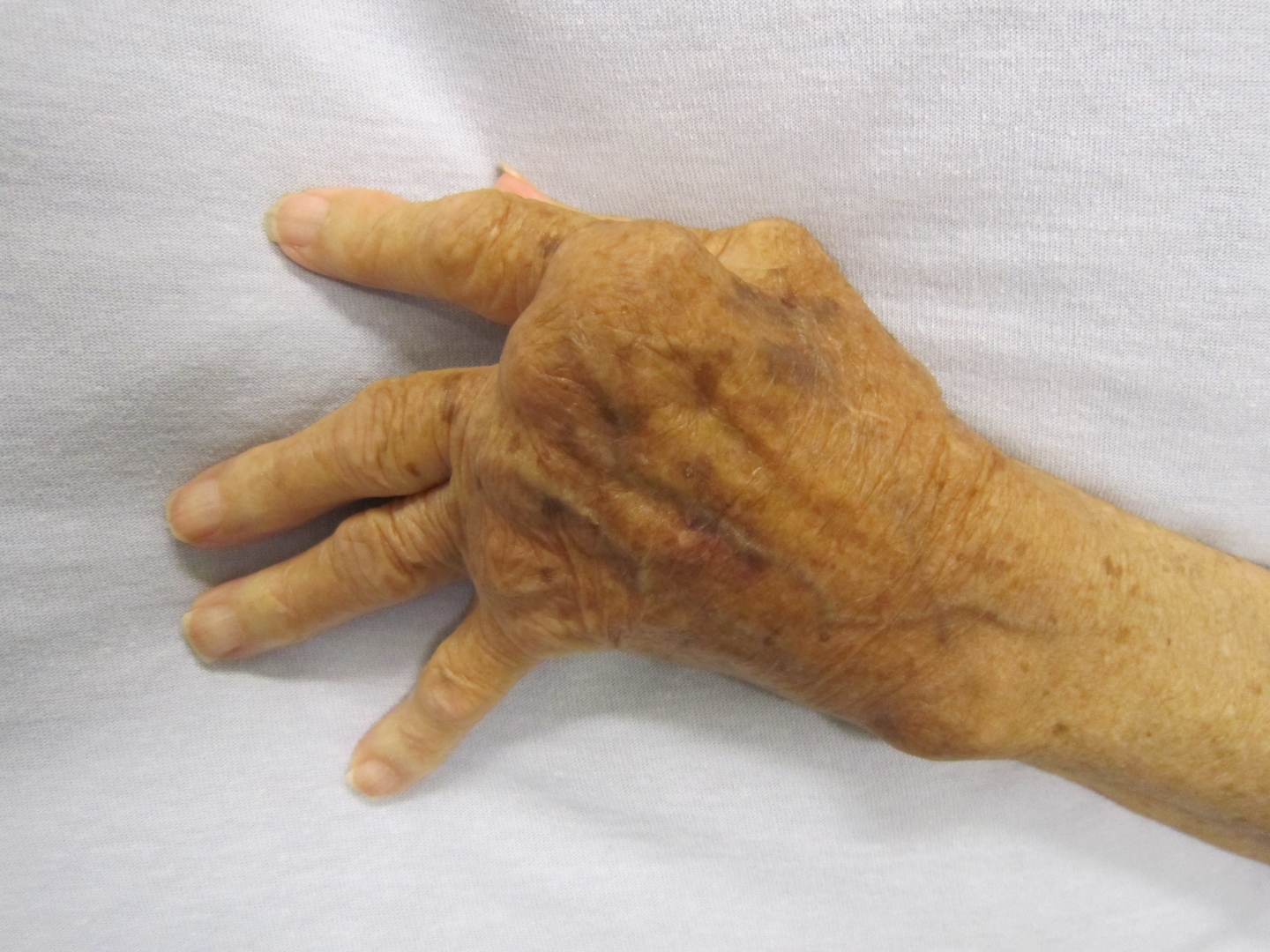
The housekeeper has synovial swelling (joint lining) in the joints of the second and third metacarpal bones of her right hand. The base of her left thumb and both wrists are also swollen. Polyarthritis.
Clinical diagnosis: rheumatoid arthritis
♦ Definition: rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease that occurs in all age groups, but usually begins between the ages of 40 and 60.
RA is three times more common in women than in men in all populations. Early RA is characterised by morning stiffness and swelling of the small joints of the hands and wrists.
In Europe and the US, the disease affects 0.8% of adults. The disease is less common in rural areas of Africa and Asia, but this is not the case in urban areas.
♦ Discussion
The hand abnormalities in Jacob Jordaens' housekeeper clearly contrast with her young, fresh appearance.
The hands of the other figures are normal. The dominant symptom of rheumatoid arthritis is symmetrical joint damage to the small peripheral joints of the hands and feet and to the large joints, namely the knees and elbows. The joint pain is inflammatory in nature, with considerable morning stiffness. The pain is due to a doughy synovial hypertrophy. The inflammation of the joint membrane (synovitis) gives the fingers a typical spindle-shaped appearance.
Tendon sheath inflammation (tenovaginitis) and bursitis are also often present. Prolonged synovitis leads to progressive joint destruction with radiologically demonstrable joint space narrowing and bone erosion. Joint destruction leads to joint instability, incomplete and complete dislocations.
Source: Jan Dequeker
The artist and the doctor look at paintings
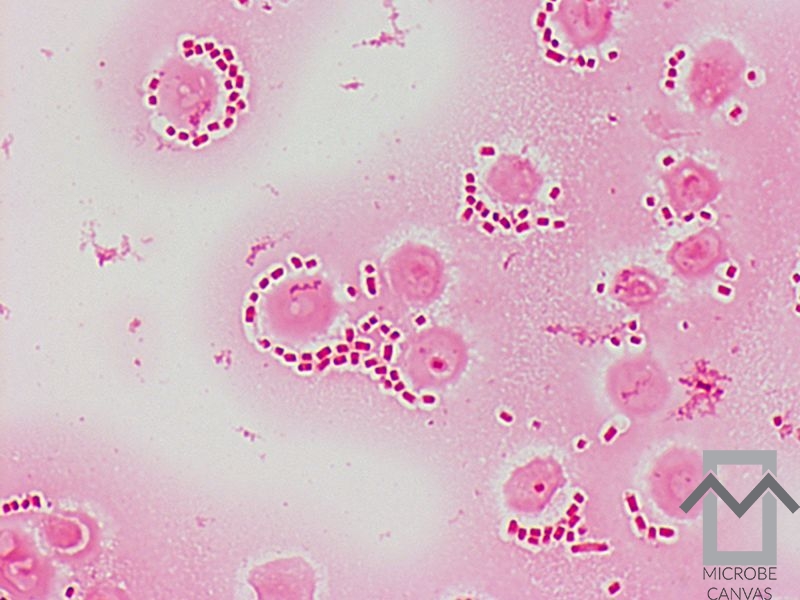
♦♦♦ Bacterial arthritis
Treatment of bacterial arthritis requires urgency because delayed treatment can lead to severe damage to the joint. The infection generally develops haematogenously (90-95%). The synovium is highly vascularised and bacteria can easily reach the joint cavity via the bloodstream.
They can also enter the joint directly, for example via a deep wound or from a focus of osteomyelitis.
The risk of bacterial arthritis depends on risk factors such as defects in the phagocyte system, impaired defence mechanisms, chronic serious diseases, direct penetration and joint damage, and the type of bacterial arthritis is
Intravenous drug users often develop septic arthritis in unusual locations (e.g. sternoclavicular or sacroiliac joints) and with bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Aseptic arthritis, joint trauma and joint surgery are important risk factors.
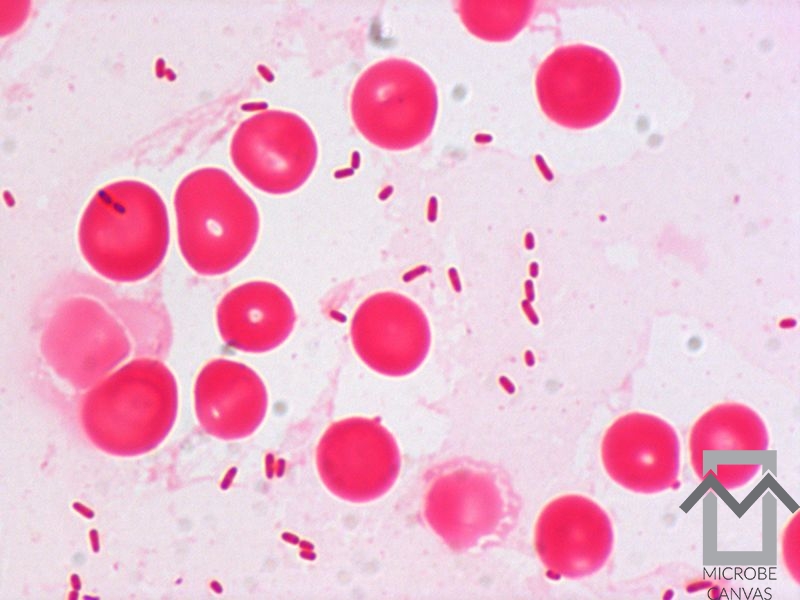
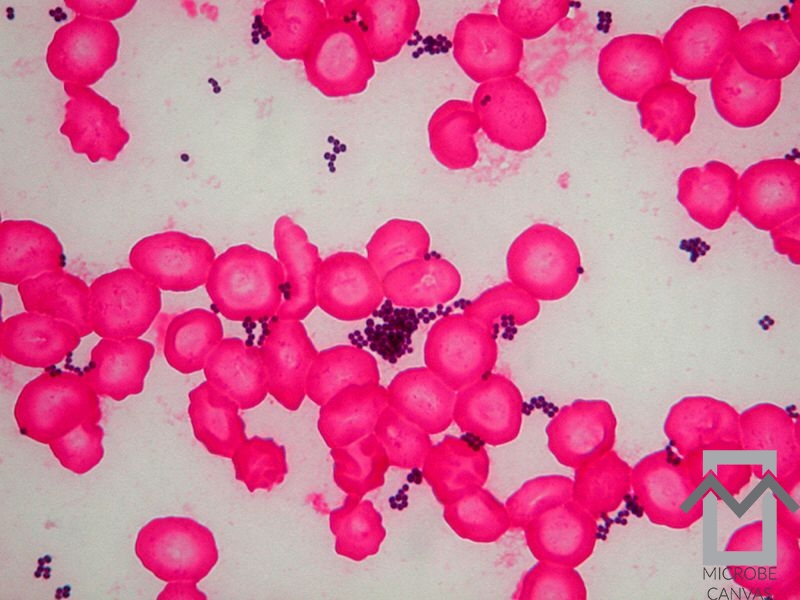
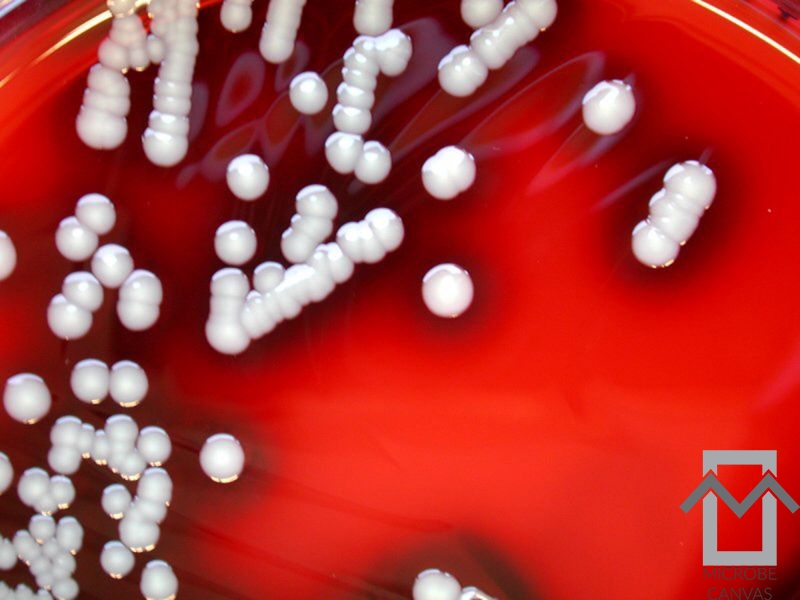
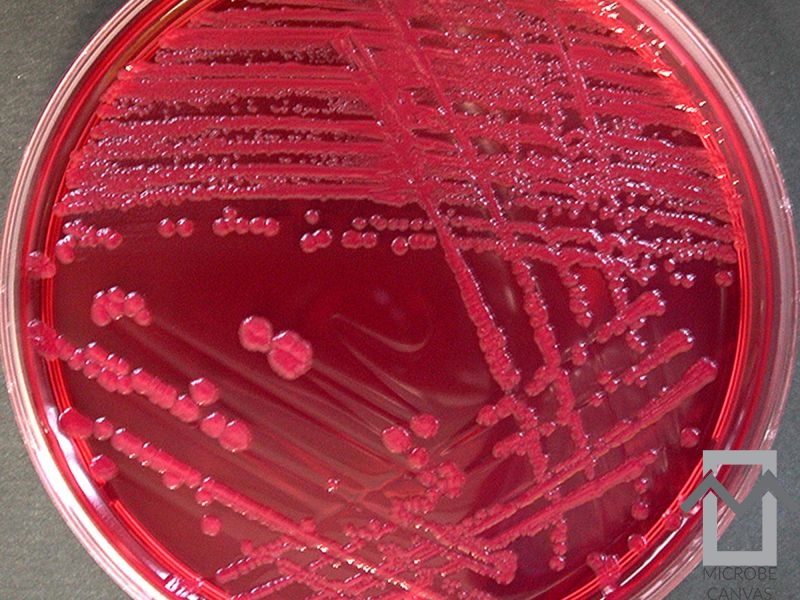
Infections with Staphylococcus aureus are by far the most common, with the percentage of infections with penicillin-resistant strains having risen significantly.
Streptococcus species and Gram-negative microorganisms are also found.
Arthritis caused by Haemophilus influenzae is often found in infants and young children.
Before the era of antibiotics, Streptococcus pneumoniae arthritis was quite common in cases of pneumonia.
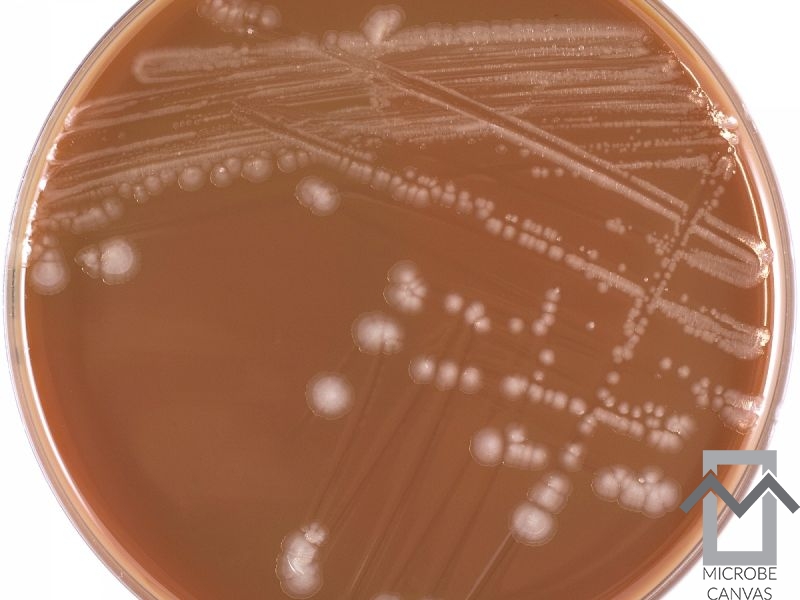
Over the last 20-30 years, arthritis caused by Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (in intravenous drug users), has been seen more often than before.
Blood cultures are often positive. In general, the condition is monoarticular, with a strong preference for the knee, followed by the ankle, wrist, shoulder and hip.
Infectious arthritis in a hip occurs almost exclusively in a hip with an artificial joint.
In the absence of immediately identifiable causes, one must look for a focus, such as wounds, ingrown toenails, etc.
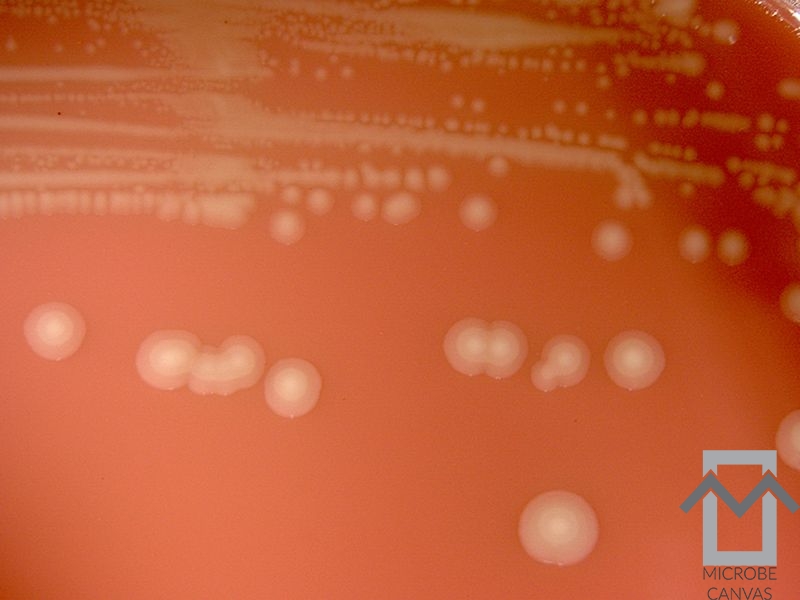
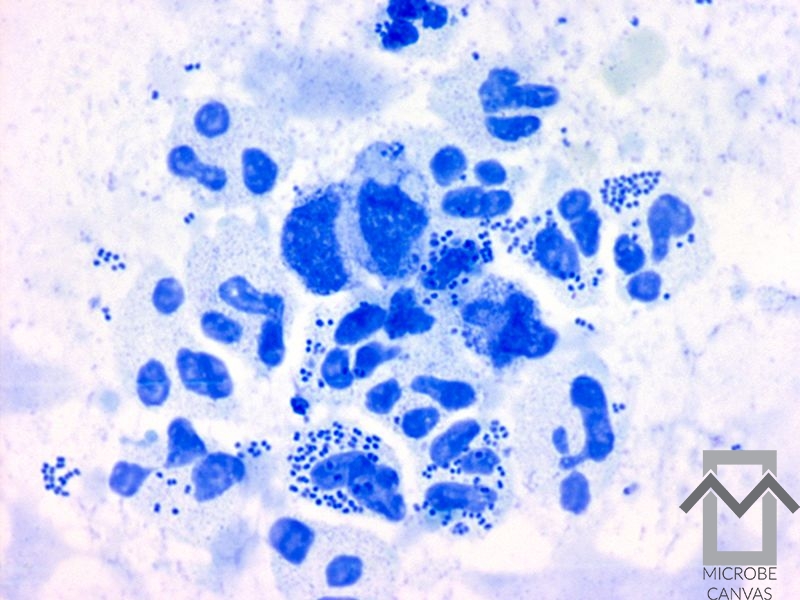
Gonococcal arthritis
This is the most common form of infectious arthritis in patients younger than 50 years of age.
It usually affects women, who are particularly susceptible to this infection around the time of the menopause and during pregnancy.
Neisseria gonorrhoeae can be cultured from the joint fluid in only a small percentage of patients. It is more often cultured from the urethra, vagina, cervix, rectum or throat.
Consultation with a bacteriologist is recommended in order to obtain the best possible results from the examination. In addition to the presence of tenosynovitis in arthritis (which distinguishes gonococcal arthritis from Reiter's disease), factors that may lead us to the diagnosis include fever and a rash localised on the trunk or limbs, consisting of a small number of non-itchy vesicles, pustules and purpura. Prodromal symptoms, such as arthralgia, are mainly observed in the wrists and fingers. Patients in whom the bacterium is cultured from the joint fluid often have knee involvement, and sometimes wrist or ankle involvement. Loes van Damme
Medische Microbiologie & Infectieziekten (MMIZ)
Erasmus MC - Rotterdam
Artritis reumatoïde
References
Jan Dequeker
The artist and the doctor look at paintings
Medische Microbiologie & Infectieziekten (MMIZ)
Erasmus MC, Rotterdam
Photo's
Wikipedia
Wikipedia.org

Art lijst
Schilderijen
- Bosch, Hieronymus – The Peddler
- Bosch, Hieronymus_The Haywain triptych
- Botticelli, Sandro_Primavera / Spring
- Brueghel the Elder, Pieter – The Tower of Babel
- Campin, Robert — Mérode Triptych
- Courbet, Gustave_The painters Studio
- Dali, Salvadore_The Temptation of Saint Anthony
- Dou, Gerard_the Quack Doctor
- Eyck van Barthélemy_Still life with books
- Fra Angelico_Annunciation
- Géricault, Théodore_Medusas raft
- Magritte, Rene_Prohibited to depict
- Matsys, Quinten_The money changer and his wife
- Memling, Hans_Two horses in a landscape
- Picasso, Pablo_Guernica
- Rembrandt_Abraham en de drie engelen
- Rembrandt_Elsje Christiaens
- Unknown – 16th century: Four depictions of a physician
- Velazquez, Diego_Las Meninas
Schilderijen en de dokter
- Agenesia Sacrale (a rare congenital disorder in which the fetal development of the lower spine)
- Alopecia areata (hair loss)
- Arthrogryposis congenita (birth defect, joints contracted)
- Artritis psoriatica (inflammatory disease of the joint)
- Artritis reumatoïde
- Breast development (delayed)
- Bubonic plague
- Diphtheria
- Eye surgery
- Gigantism and Acromegaly
- Goiter (struma)
- Hare lip (cheiloschisis) / cleft palate
- Herpes zoster (shingles)
- Hunger edema
- Influenza Epidemic of 1858
- Insanity - Malle Babbe (1640)
- Leprosy
- Lovesick, pregnancy
- Lymph node tumor (lymphoma), non-Hodgkin
- Manic Depression Psychosis
- Measles / Rubella? (acute viral infection)
- Melanoma or nevus (birthmark)
- Membranous glomerulonephritis
- Murder (pneumothorax, arterial bleeding)
- Neurofibromatosis
- Osteoartrose / hallux valgus
- Osteomyelitis
- Otitis media (acute middenoorontsteking)
- Parotitis (mumps)
- Platvoet en Spitsvoet
- Polio
- Prepatellaire bursitis
- Progeria
- Pseudohermafroditisme
- Pseudozwangerschap
- Psychoneurose (acute)
- Rachitische borst
- Reumatische koorts (acute)
- Rhinophyma of knobbelneus
- Rhinophyma rosacea_depressie
- Rhinoscleroma
- Schimmelziekte_Favus
- Syfilis (harde 'sjanker')
- Tandcariërs
- The Extraction of the Stone of Madness
- Tuberculose long
- Ziekte van Paget
Schilders
Historie lijst
- 1632-1723_Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
- 1749-1823_Edward Jenner
- 1818-1865_Ignaz Semmelweis
- 1822-1895_Louis Pasteur
Wetenswaardigheden lijst
- 1887 Psychiatric Hospital
- Animals on duty
- Bizarre advice for parents
- Bloodletting
- Bloodthirsty Hungarian Countess Elizabeth Báthory (1560–1614)
- Butler escaped punishment three times.
- Dance mania / Saint Vitus Dance
- Doctors’ advice did more harm than good
- French Revolution Louis XVI
- Frontal syndrome (Phineas Gage)
- Heart disease (Egyptian princess)
- Ice Age (minor)_1300-1850
- Ivan IV de Verschrikkelijke (1530-1584)
- Kindermishandeling
- Koketteren met koningin Victoria
- Koningin door huidcrème vergiftigd
- Kraambedpsychose (Margery Kempe)
- Massacre in Beirut
- ME stonden bol van de seks
- Mummie bij de dokter
- Plee, Gemak of Kakstoel
- Prostaatkanker (mummie)
- Sexhandel in Londen
- Swaddling baby
- Syfilis was in de mode
- Testikels opofferen
- Tropische ziekten werden veroveraars fataal
- Vrouwen als beul in WOII
- Wie mooi wil zijn moet pijn lijden
- Zonnekoning woonde in een zwijnenstal