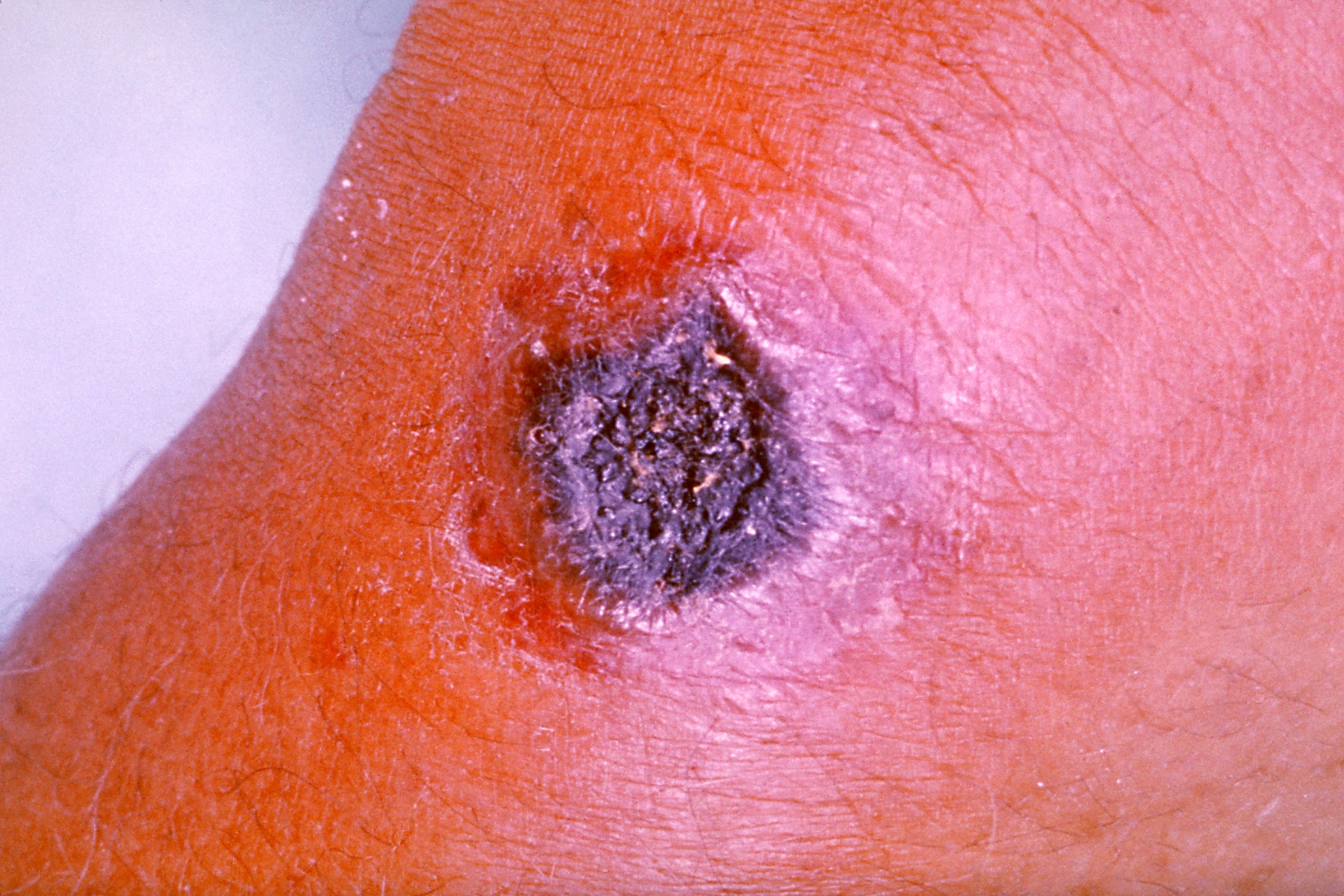
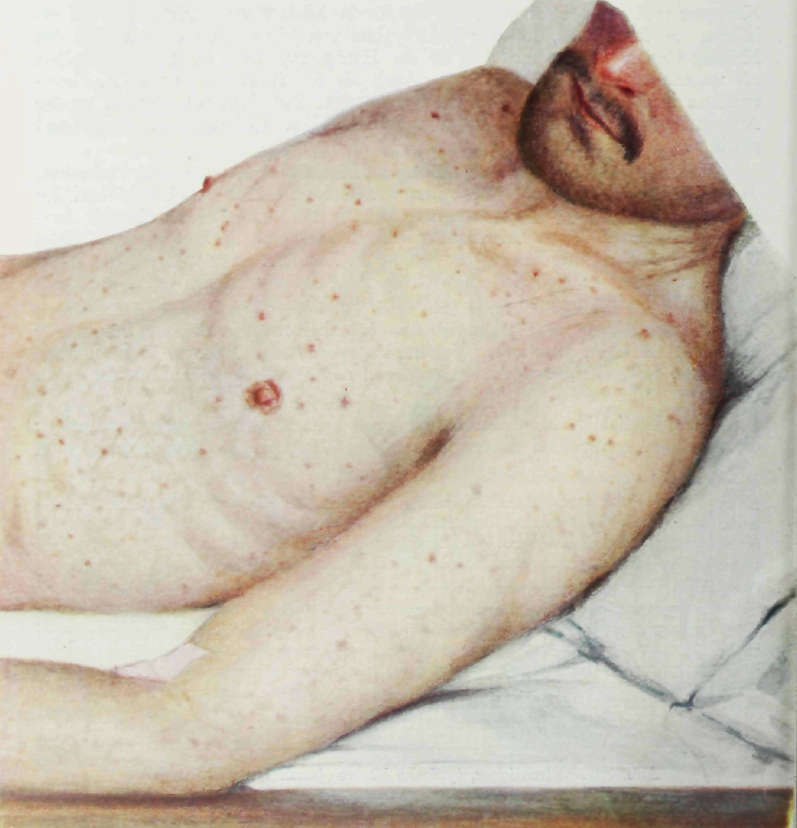
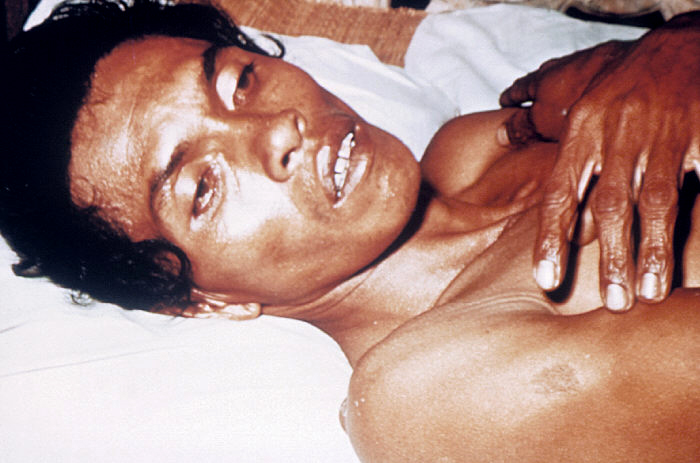
Typhoid fever (Epidemic typhus)
Other names: camp fever, jail fever, hospital fever, ship fever, petechial fever, epidemic louse-born typhus. Epidemic typhus, also known as louse-borne typhus, is a form of typhus so named because the disease often causes epidemics following wars and natural disasters where civil life is disrupted. Epidemic typhus is spread to people through contact with infected body lice, in contrast to endemic typhus which is usually transmitted by fleas. Though typhus has been responsible for millions of deaths throughout history, it is still considered a rare disease that occurs mainly in populations tha…







.jpg)

.png)