SEARCH
Search
CAMP-test_Listeria monocytogenes & L. ivanovii
-
General
The CAMP-test can be used to differentiate among hemolytic Listeria species.
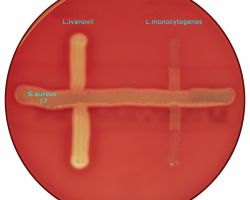
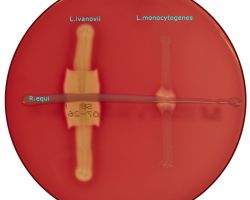
The test is carried out by streaking a beta-hemolysis producing Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923) strain and Rhodococcus equi parallel to each other on a blood agar plate.
Suspect cultures are streaked at right angles in between (but not touching) the two streakes.
Hemolysis by L. monocytogenes and to a lesser degree L. seeligeri is enhanced in the vicinity of S. aureus, and hemolysis by L. ivanovii is enhanced in the vicinity of the R. equi streak.
However, the reliability of the CAMP-test is limited.
-
History
The CAMP factor reaction was first described in 1944 by Christie, Atkins and Munch-Peterson and reverse to the synergistic lysis of erythrocytes by the beta hemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus and the extra cellular CFB protein of Streptococcus agalactiae.
-
Related
-
References
Manual of Clinical Microbiology
10th edetion
James Versalovic et all
Foto's
MMIZ
ErasmusMC
Rotterdam