Listeria ivanovii
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Listeriaceae
Of the seven species within the genus Listeria, only L. monocytogenes and L. ivanovii are pathogenic.
Natural habitats
They are widely distributed in the environment
Clinical significance
Listeria ivanovii is primarily a pathogen of ruminants.
Systemic infections in immunodeficiency virus-infected and non-immunosuppressed patients have, however been described.
-
Diseases
-
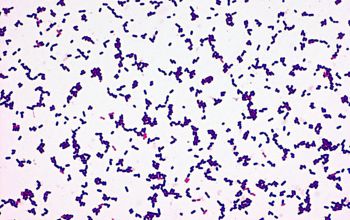
Gram stain
Regular, short gram positive rods,
0.4-0.5 x 0.5-2.0 µm,
that occur singly or in short chains.
Filaments of 6-20 µm, may occur in older or rough cultures.
Listeria may be confused with members of the coryneform rods (especially in direct slides from blood cultures), since the cells may be arranged in V forms or palisades.
-
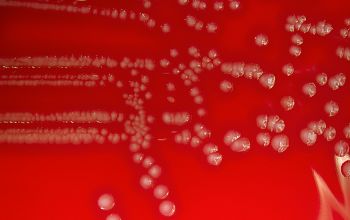
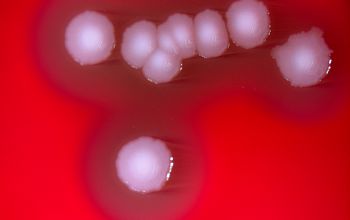
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
5% CO2 stimulates growth
BA: colonies are small, smooth, white-grey and produce a wide zone of hemolysis.
McConkey: growth
BBAØ: growth
CAMP-test
L.ivanovii ►CAMP-test negative (S.aureus streak)
L.ivanovii ►CAMP-test positive (R.equi streak = a shovel shape)
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition