Gordonia bronchialis
-
General information
Formerly called Rhodococcus bronchialis
Taxonomy
Family: Gordoniaceae
Natural habitats
In the environment, soil, marine sediments and wastewater systems.
Infection is primarily by inhalation of the bacteria.
Clinical significance
Are rarely found in humans. Pathogenicity is unknown.
This organism is known to cause infections in immunocompromised and immunocompetent hosts.
It can cause, skin infections, chronic pulmonary disease, catheter-related sepsis, wound infections and b septicemia.
-
Gram stain
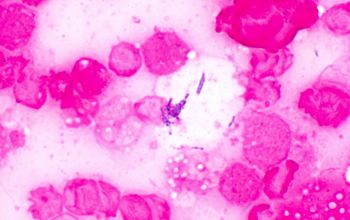
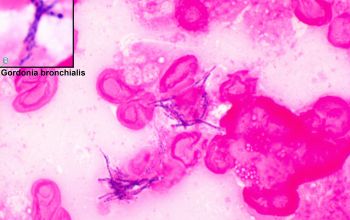
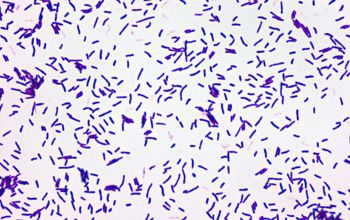
Gram positive rods, short rods and cocci,
0.5-1.0 x 1.0-2.5µm,
which resemble thin beaded coccobacilli.
They occur singly, in pairs, in V-shaped arrangements, or as short chains.
Rod-coccus life cycle.
Cells in early growth phase are rods and those in exponential phase are cocci.
Elementary branched hyphae which fragments into rod- and coccoid-like elements are formed by some species.
They stain Gram positive or Gram variable
Could easily be mistaken for a component of the normal oral biota in sputum specimens
modified Kinyoun usually partially acid fast
-
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate aerobic
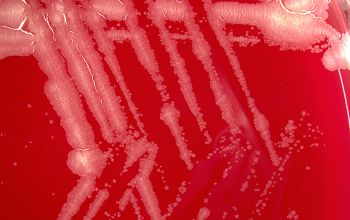
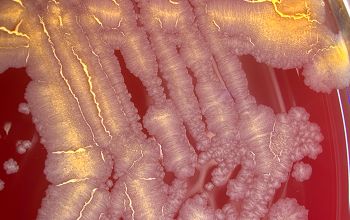
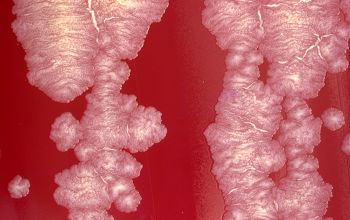
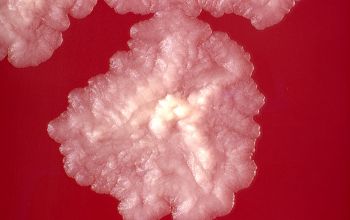
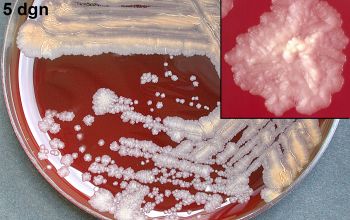
BA: after 2-5 days colonies are rough, wrinkled, beige, brownish, salmon to pink or orange to red, particularly on chocolate agar
Cultures showing smooth colonies can generate rough colonies, a change which seems to be irreversible.
Aerial hyphae negative
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition