Bacillus pumilus
-
General information
B.licheniformis, B.subtilis, B. amyloliquefaciens and B.pumilus comprise the subtilis group, which has been associated with food borne gastro-enteritis
Taxonomy
Family: Bacillaceae
Natural habitats
Spores occur in soil, on bird feathers, may survive severe heat treatment
Clinical significance:
Bacillus pumilus is generally considered non-pathogenic but can occasionally cause opportunistic infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
Clinical significance includes:
- Wound infections: Rare cases have been reported, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Bacteremia: It has been linked to bloodstream infections in some cases, primarily in hospitalized patients.
- Contamination: B. pumilus can also be a contaminant in clinical samples and laboratory settings.
Although rarely pathogenic, B. pumilus is of interest for its potential in industrial applications, such as in the production of enzymes.
-
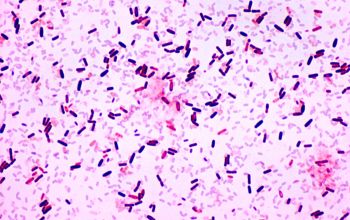
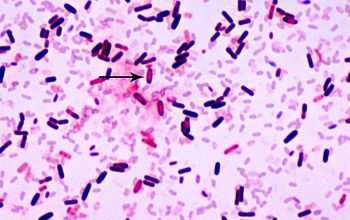
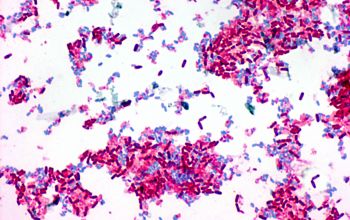
Gram stain
Gram positive, or Gram variable
0.6-0.7 x 2.0-3.0 µm
Spore shape: ellipsoidal / cylindrical
Spore position: central, paracentral or subterminal
Sporangia swelling: negative
-
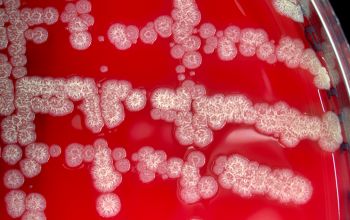
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate aerobic
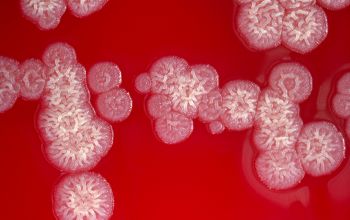
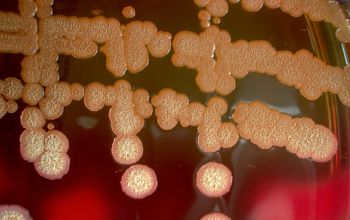
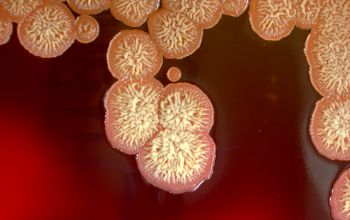
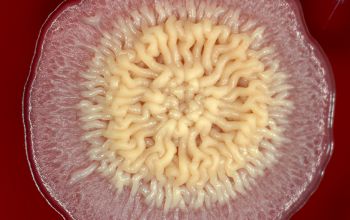
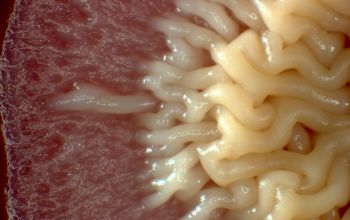
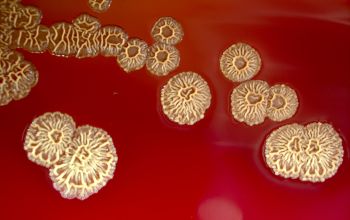
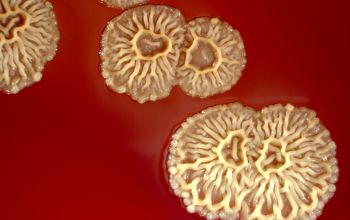
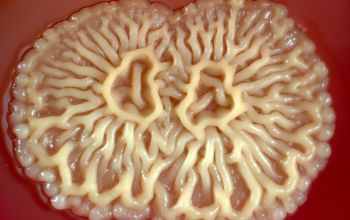
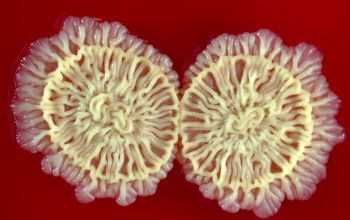
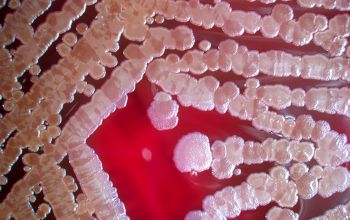
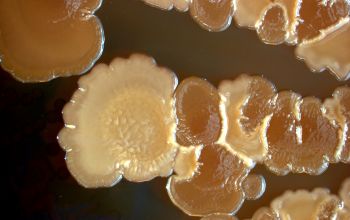
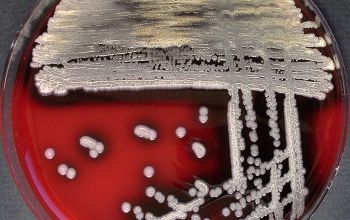
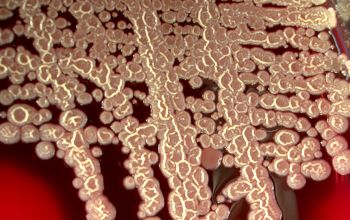
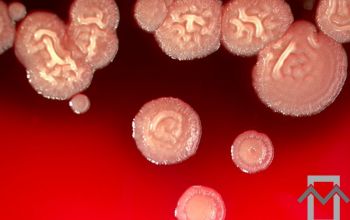
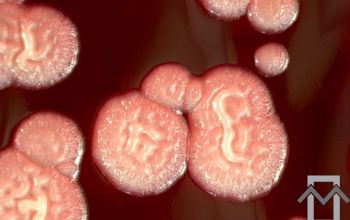
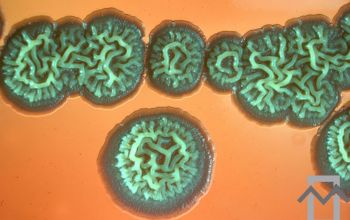
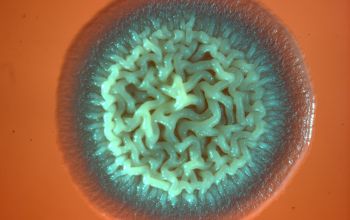
BA: colonial morphology is variable.
Colonies maybe wrinkled and irregular and they are unpigmented and most are opaque or smooth and become yellowish-brown and hemolysis is variable
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition