It produces a crystalline protein body pathogenic for the larvae of Lepidoptera.
It is used as a biological insecticide.
www.biotecharticles.com
Bacillus thuringiensis
-
General information
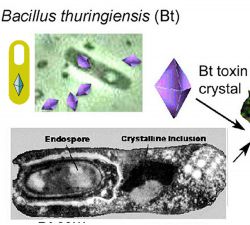
Bacillus thuringiensis is distinguished by its characteristic parasporal crystals
Taxonomy
Family: Bacillaceae
Bacillus cereus group: B. anthracis, B. cereus, B. mycoides, B. thuringiensis
Natural habitats
Endospores are widespread in soil and many other environments.
The organism had been isolated from all continents, including Antartica.
Used as bio pesticide
Clinical significance
Bacillus thuringiensis is primarily known for its use as a biopesticide due to its production of insecticidal proteins (Cry toxins).
While it is not typically pathogenic to humans, it can cause rare infections in immunocompromised individuals, such as:
- Wound infections: In individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Bacteremia: Very rarely reported in clinical settings.
B. thuringiensis is more clinically significant as a biocontrol agent in agriculture rather than as a human pathogen. Its antibiotic susceptibility and potential for causing infections are minimal in healthy individuals.
-
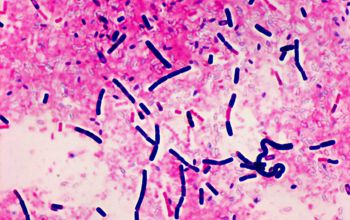
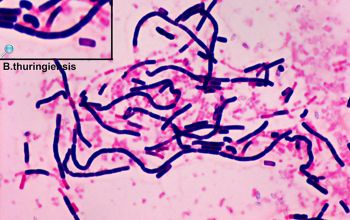
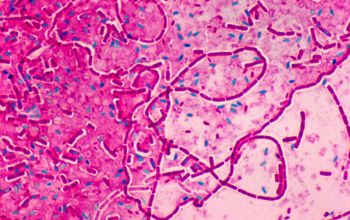
Gram stain
Large Gram positive (variable) rods,
1.1-1.2 x 3.0-6.0 µm
(only B.cereus + B.megaterium group >1 µm)
The bacilli tend to occur in chains
Spore shape: ellipsoidal
Spore position: central, paracentral or subterminal
Sporangium swollen: negative
Spores may lie obliquely in the sporangia
Parasporal bodies within the sporangia.
These crystalline protein inclusions may be bipyramidal, cuboid, spherical to ovoid, flat rectangular or heteromorphic in shape.
They are formed outside the exosporium and readily separate from the liberated spore.
They are known as delta-endotoxins or insecticidal crystal proteins.
The bacilli tend to occur in chains
Capsule not present
-
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
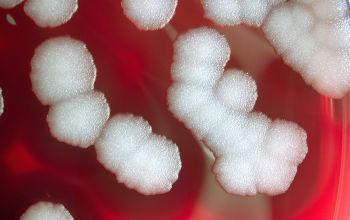
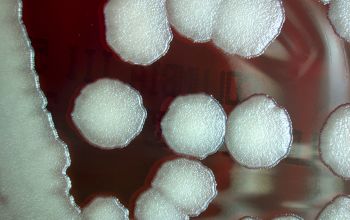
BA: they are usually whitish to cream in color, large 2-7 mm, and vary in shape from circular to irregular with entire to undulate, crenate or fimbriate edges and they usually have matt or granular textures.
Sometimes smooth and moist colonies may appear.
Hemolytic
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition