Bacillus mycoides
-
General information
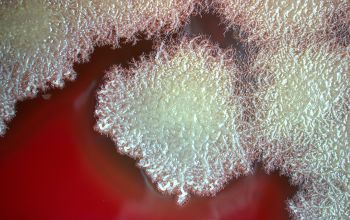
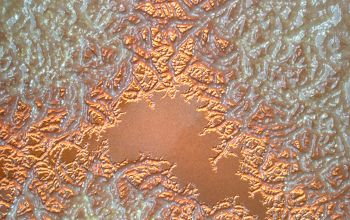
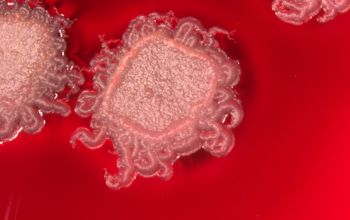
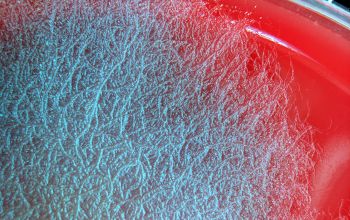
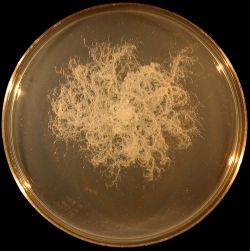
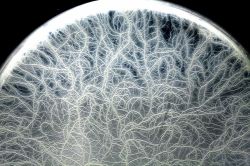
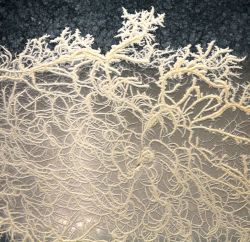
Bacillus mycoides is distinguished by its characteristic rhizoid colonies and absence of motility.
Taxonomy
Family: Bacillaceae
Bacillus cereus group: B.anthracis, B.cereus, B.mycoides, B.thuringiensis
Natural habitats
Spores are widespread, soil, water, air foods etc
Clinical significance
Bacillus mycoides is generally considered non-pathogenic but has been occasionally linked to opportunistic infections in immunocompromised individuals, including:
- Wound infections: Rare cases have been reported, often in patients with pre-existing health conditions.
- Contamination: Due to its environmental prevalence, B. mycoides can also be a contaminant in clinical specimens.
Its clinical significance is limited, and infections are relatively uncommon.
The bacterium is often susceptible to a variety of antibiotics.
-
Gram stain
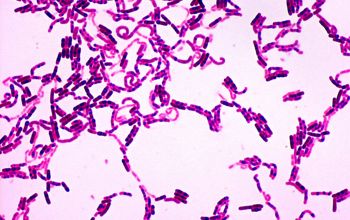
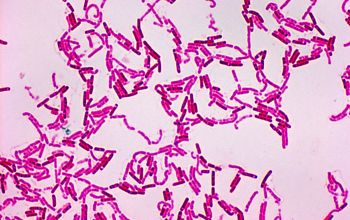
Large Gram negative, rarely positive or variable rods
1.0-1.2 x 3.0-5.0 µm
(only B.cereus group + B.megaterium >1 µm)
The bacilli tend to occur in chains
Spore shape: ellipsoidal
Spore position: central, paracentral or subterminal
Sporangium swollen: negative
Capsule: not present
-
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
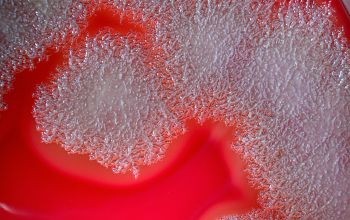
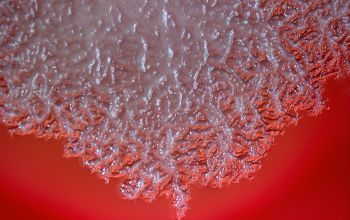
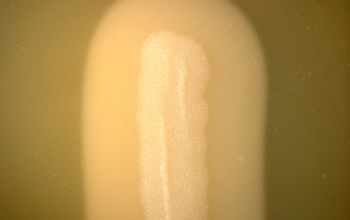
BA: colonies are white to cream, opaque and characteristically rhizoid, adherent and ß-hemolytic.
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition photo: wikipedia