Is a virus that infects and replicates within a bacterium
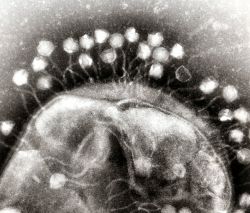
EM of bacteriophages attached to a bacterial cell.
Dr Graham Beardshttps://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Phage.jpg
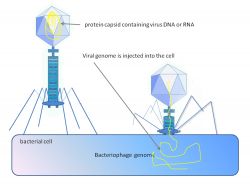
phage injecting its genome intobacterial cell
Graham Colmhttps://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Phage_injecting_its_genome_into_bacterial_cell.png
Brevibacterium casei
-
General information
More than 90% of all clinical Brevibacterium are B. casei.
Taxonomy
Family: Brevibacteriaceae
Natural habitats
They are inhabitants of the human skin and can be found in dairy products, fresh and salt water, soil, sewage, fruits, vegetables and rice paddies.
Clinical significance
Rarely causes infection and then only in immunocompromised patients such as, osteomyelitis, peritonitis, bacteremia and malodorous feet
Malodorous feet
Sweat and bacteria is the cause of foot odor.
The most common bacteria Brevibacterium causes smelly feet.
Food odor usually appears to smell cheesy, similar to the smell of ammonia.
They are active on the soles of feet and between the toes.
The bacteria convert methionine to methanethiol, which smells like sulphur, that gives out the foul smell.
-
Gram stain
Short, coryneform, Gram positive rod,
0.6-1.2 x 1.5-6 µm
they are arranged singley or in pairs,and often in an angle to give "V" formations
in older cultures (3-7 days) segmenting the rods into cocci, and easy decolorization
(rod-coc cycle)
-
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate Aerobic
BA: colonies are smooth and may be white to gray-white, yellow or orange-red depening on the species,
and are convex, mostly creamy, and 2 mm or greater after 24 h.
Pigment production is light dependent.
These organism have a distingtive odor sometimes described as cheesy or body odor.
McConkey: grow poorly or not at all
BBAØ: no growth
Smell
many of them have a distinctive cheese-like odor
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition