Corynebacterium accolens
-
General information
The pathogenic potential of coryneform bacteria has been underestimated
Taxonomy
Family: Corynebacteriaceae
Natural habitats
They are part of the normal biota of the skin and mucous membranes in humans and other mammals.
Clinical significance
C. accolens is found in specimens from the eyes, ears, nose, and oropharynx.
Evidence confirming the Corynebacterium isolates as the causative agents of these infection is not provided
Endocarditis of native aortic and mitral valves due to this agent has been described.
-
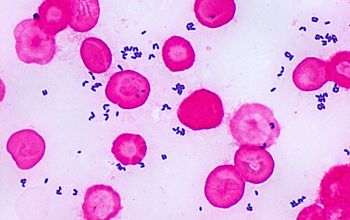
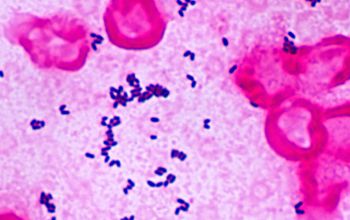
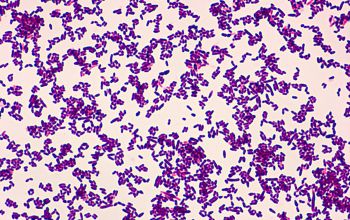
Gram stain
Gram positive rods,
irregularly shaped (‘coryneforms”),
they are arranged as single cells, in pairs, in V forms, in palisades, or in clusters with
a so-called Chinese-letter appearance.
Club-shaped rods are observed in true members of the genus Corynebacterium only
-
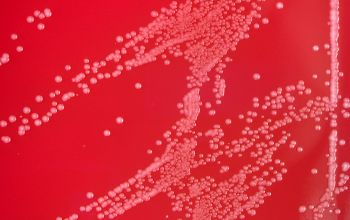
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
BA: colonies are convex, smooth, and < 0.5 mm in diameter. (lipophyl)
They exhibited satellitism when grown in the presence of staphylococcal colonies, which may be suggestive of their lipophilic nature.
Lipophilic
bacteria (fat-liking bacteria) are bacteria that proliferate in lipids.
Good growth is observed with broth supplemented with 1% Tween 80
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition
Clinical Microbiology of Coryneform Bacteria Guido Funke, Clin Microbiol Reviews, jan 1997