Rothia dentocariosa
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family:Micrococcaceae
Natural habitats
Is a normal in habitant of the mouth and upper respiratory tract.
Clinical significance
Isolated from dental carries and very rarely cause disease.
The most common infection is endocarditis, in people with underlying heart valve disorder.
-
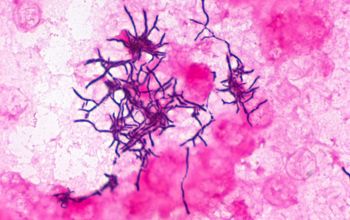
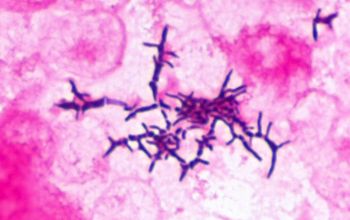
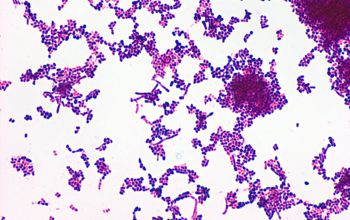
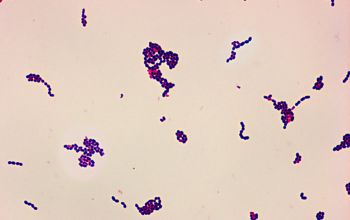
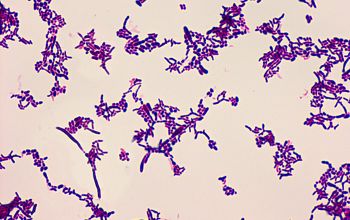
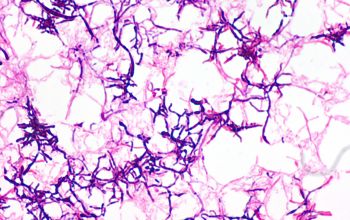
Gram stain
Gram positive pleomorphic rods with branching, filamentous and diphteroid forms.
Agar: mixture of cocci and rods, rarely filaments
Broth: they are going to branch out after an incubation period of some days
-
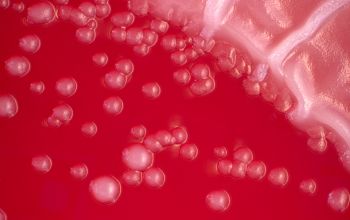
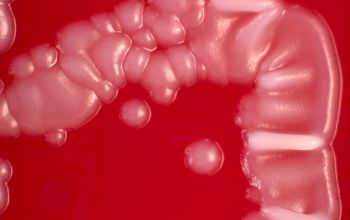
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
They grow slightly better in 5% CO2.
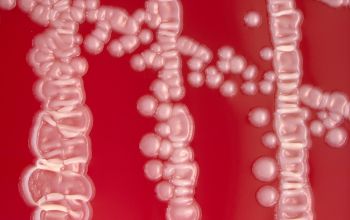
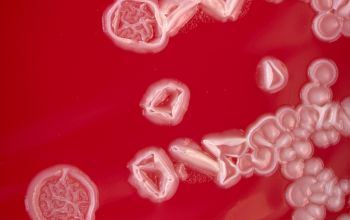
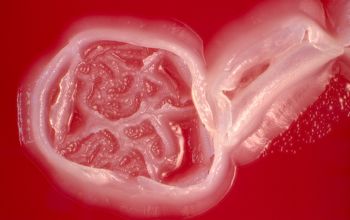
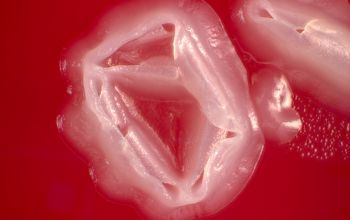
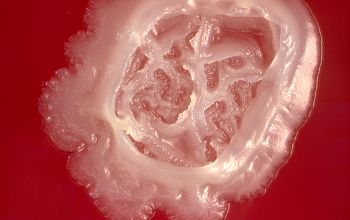
BA: colonies are typically whitish (or, more rarely, grayish black), raised, and smooth or rough or have a spooked-wheel form, and they are up to 2 mm after 48h.
Both colony forms can occur in the same culture.
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition