Cellulosimicrobium cellulans
-
General information
Formerly known as Oerskovia xanthineolytica
Taxonomy
Family: Promicromonosporaceae
Former name: Oerskovia xanthineolytica
Natural habitats
The environment like the soil, water, decaying plant material.
Clinical significance
Rarely cause human infections.
Infections mainly occur in immunocompromised patients and very often associated with a foreign body.
-
Gram stain
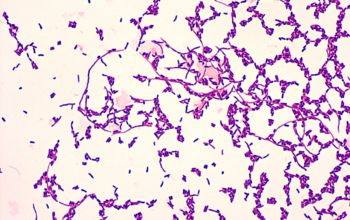
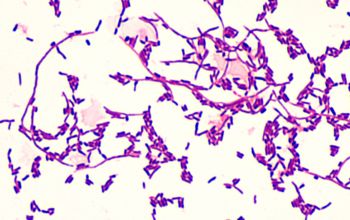
Gram positive rods,
highly branched, pleomorphic and filamentous.
After a long incubation period, they fragment into coccoid rods
Older cultures decolorize easier.
Liquid
Gram positive rods, pleomorphic, filamentous and branching.
Culture
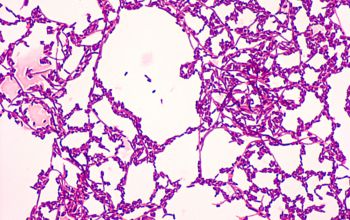
Gram positive rods, more coccoid rods
Upon reduction of available food (carbohydrates) the rods are even shorter or coccoid
Kinyoun: negative
-
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
5% CO2 enhanced growth
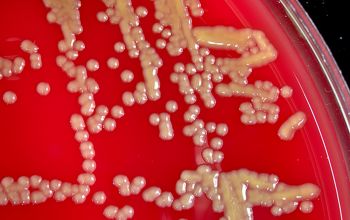
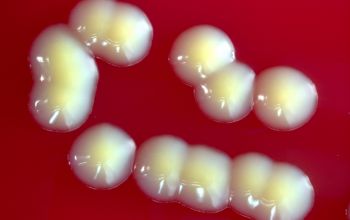
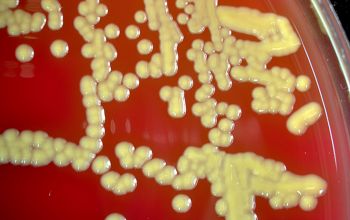
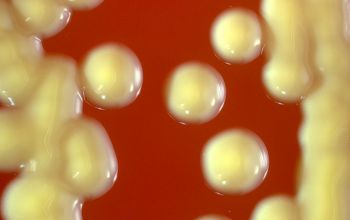
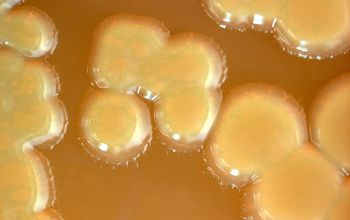
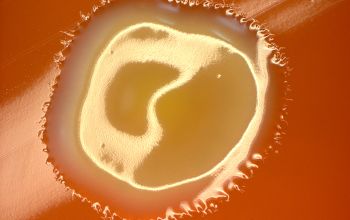
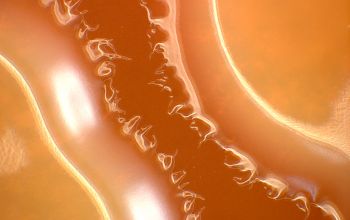
BA: colonies are not hemolytic, pale yellow to phosphorous yellow, convex, and creamy, they penetrate into the agar (“substrate hyphae”) and are 1-2 mm after 24h.
After 5-7 days, the colonies became fringed
Substrate hyphae: positive (after 5-7 days)
Aerial hyphae: negative
BBAØ: growth
Some strains are obligate aerobic
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition