Ignaz Semmelweis (1818-1865)
was a Hungarian physician whose work demonstrated that hand-washing could drastically reduce the number of women dying after childbirth.
This work took place in the 1840s, while he was Director of the maternity clinic at the Vienna General Hospital in Austria.
Streptococcus pyogenes
-
General information
Streptococcus pyogenes = Lancefield Group A
Taxonomy
Family: Streptococcaceae
Natural habitats
Colonizes the human throat and skin and has developed complex virulence mechanism to avoid host defenses.
Clinical significance
The upper respiratory tract and skin lesions serve as primary focal sites of infections and principal reservoirs of transmission.
They can cause superficial or deep infections due to toxin-mediated and immunologically mediated mechanisms of disease.
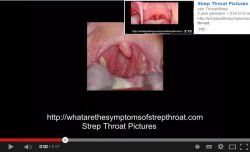
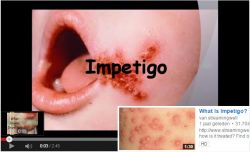
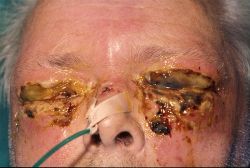
S. pyogenes is the most common cause of bacterial pharyngitis and impetigo.
In the past, S. pyogenes was a common cause of childbed fever of puerperal sepsis.
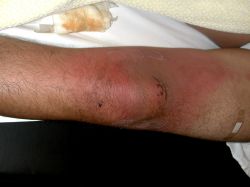
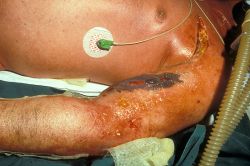
They are responsible for deep or invasive infections, especially bacteremia, sepsis, deep soft tissue infections, such as erysipelas, cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis.
Less common myositis, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, pneumonia, meningitis, endocarditis, pericarditis, and severe neonatal infections following intrapartum transmission.
-
Diseases
-
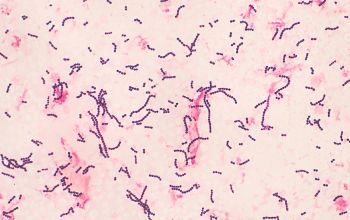
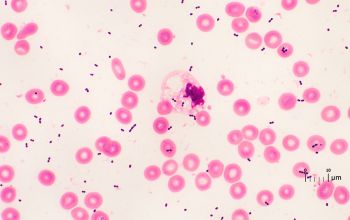
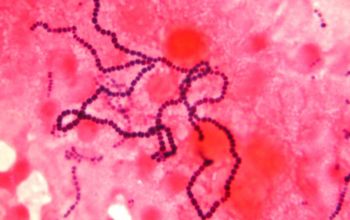
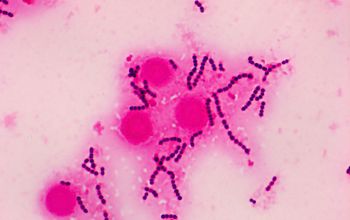
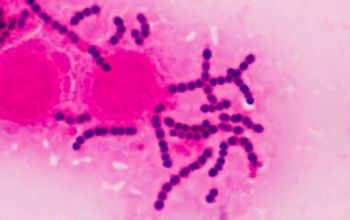
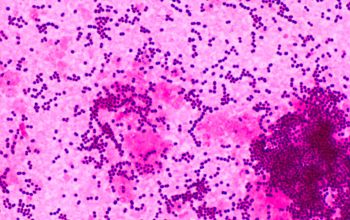
Gram stain
Gram positive streptococci,
0.6-1 µm
grouped in pairs, short to long chains,
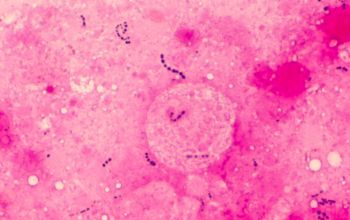
Liquid medium,
they are found in the form of chains of different lengths.
They namely divide into one direction.
-
Culture characteristics
-
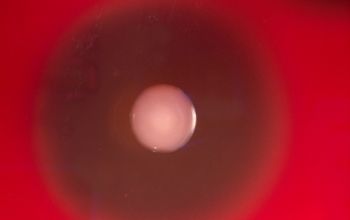
Beta-hemolytic streptococci of the pyogenic group
(S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, and S. dysgalactiae ssp equisimilis)
form colonies > 0.5 mm
Viridans streptococci form colonies < 0.5 mm
Facultative anaerobic
5% CO2 improves the growth
BA: colonies > 0.5 mm after 24 hours of incubation.
They appear grey or almost white, moist or glistening and β-hemolytic.
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition