Streptococcus mutans endocarditis: beware of the "difteroid"
S.Schelenz MD MRCPath
Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine
vol 98 sept 2005
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1199641/pdf/00980420.pdf
Streptococcus mutans
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Streptococcaceae
Streptococcus mutans group / Lancefield Group F
- S. mutans
- S. sobrinus
(S.criceti, S.ratti, S.downei)
Natural habitats
Commensals of the oral cavity.
Clinical significance
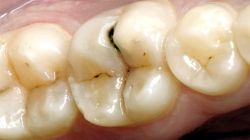
Is the major cause of dental caries and endocarditis.
S. mutans metabolizes sucrose to produce polysaccharides that help them cohere to one another forming plaque.
The combination of this plaque and acids released by S. mutans leads to the breakdown / dissolve of tooth enamel resulting in dental caries.
They are easily dismissed as a common non-pathogenic skin bacterial contaminant termed “diphteroid”
-
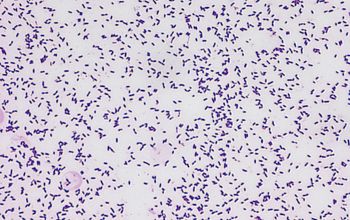
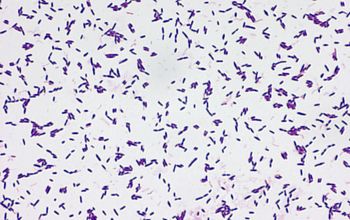
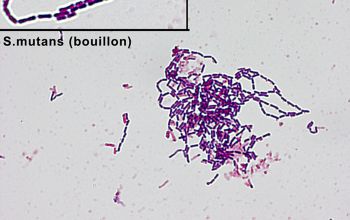
Gram stain
Gram positive streptococci,
grouped in chains OR rod-shaped (difteroid)
They appear rod-shaped on acid culture medium, but show a streptococcal appearance, in chains, when subcultured into a neutral or alkaline broth.
S. mutans may display cellular dimorphism, forming cocci under optimal growth conditions but short rods on agar media and in acidic liquid media.
(variation of morphology with the pH of the medium)
-
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
5% CO2 improves the growth
BA: are small-colony-forming and α-hemolytic (sometimes β-hemolytic) bacteria (< 0.5 mm)
Colonies of some strains are small, hard, rough, transparent and adhesive and have the classical look of crushed (frosted) glass.
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: growth (better)
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition