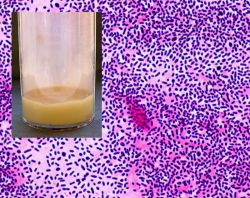
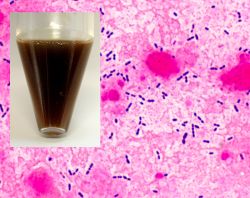
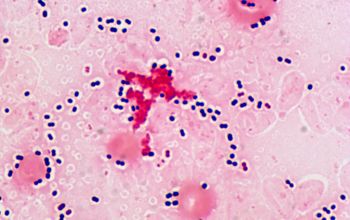
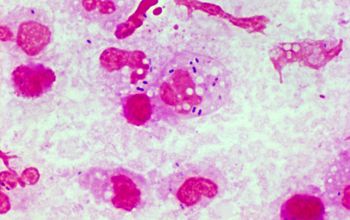
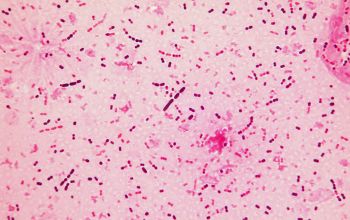
Gram stain from this sputum
sputum rufum
rust brown color (sputum rufum) is found in pneumonia, blood stains the rusty brown.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Streptococcaceae
Streptococcus mitis group / Lancefield Group F
- S. mitis
- S. cristatus
- S. oralis
- S. peroris
- S. pneumoniae
Natural habitats
Is a normal in habitant of the human upper respiratory tract, especially in children, without evidence of infection.
Clinical significance
They are the most frequently isolated respiratory pathogen in community-aquired pneumonia cases.
They can be found in peripheral blood cultures of patients. S.pneumoniae is also a major cause of meningitis, leading to high morbidity and mortality in pediatric and adult patients.
The most frequently observed infection due to S.pneumoniae is otitis media.
Other infections includes sinusitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, peritonitis, cellulitis, brain abscesses.
-
Diseases
-
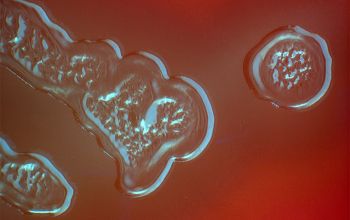
Gram stain
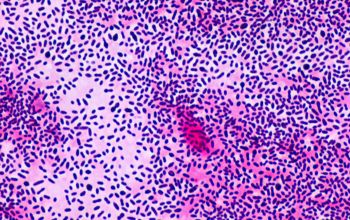
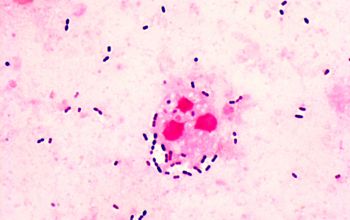
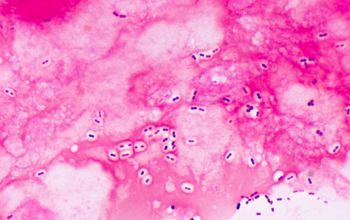
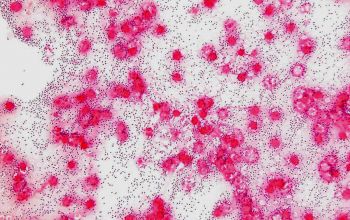
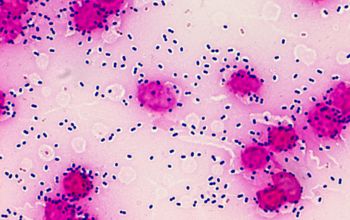
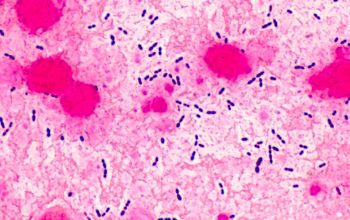
Gram positive lancet-shaped cocci,
(elongated cocci with a slightly pointed outer curvature).
They may occur intra- or extracellularly, usually,
they are seen as pairs of cocci (diplococci),
but can also occur as single or in short chains of cocci.(body fluids)
-
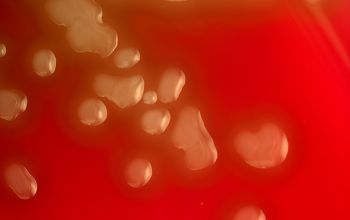
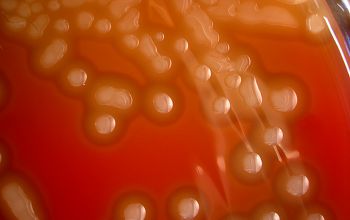
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
5% CO2 improves the growth
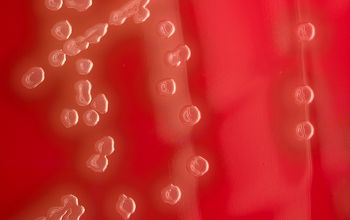
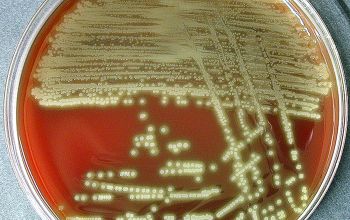
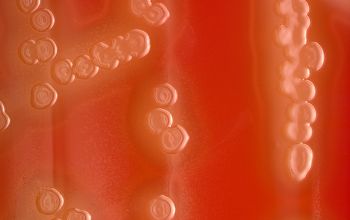
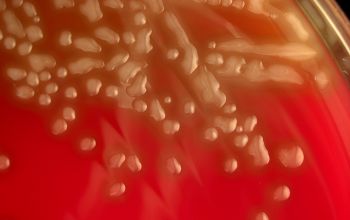
BA: appear as small, grey, moist (sometimes mucoid) colonies and produce a zone of α-hemolysis.
Once the pneumococcal culture ages 24-48 hours, the colonies become flattened, and the central portion becomes depressed, by autolysis (which does not occur with viridans streptococci)
Encapsulated pneumococci produce round, glistening colonies surrounded by a zone of α-hemolysis.
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition

-350x220.jpg)