Leuconostoc lactis
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Lactobacillaceae
Natural habitats
Found in plant material, vegetables, dairy products, and starter cultures for fermentation.
Clinical significance
Less common, but implicated in sporadic bacteremia cases.
Leuconostoc is intrinsically resistant to vancomycin
-
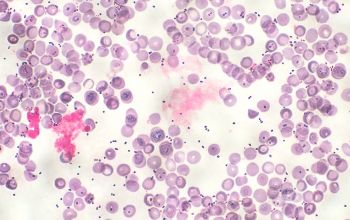
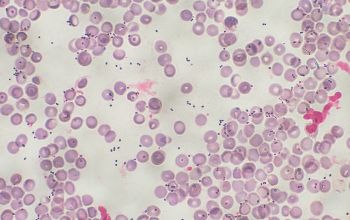
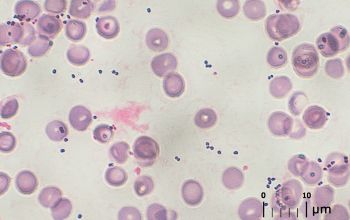
Gram stain
Gram positive coccus
0.5-0.7 x 0.7-1.2 µm
occuring in pairs and chains.
Sometimes short rods with rounded ends in long chains.
-
Culture characteristics
-
Facultatief anaeroob
BA: they produce small, gray-whitish, alpha hemolytic or nonhemolytic colonies on blood agar.
Colony morphology resembles a Streptococcus.
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition