Aerococcus urinae
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Aerococcaceae
Natural habitats
A. urinae is a rarely reported pathogen, possible due to the difficulties in the identification of the organism.
Clinical significance
Isolates of this species were originally isolated from the urine of (older) patients with urinary tract infections and were denoted Aerococcus-like organisms.
Infections with this bacterium has likely been underestimated.
A. urinae may also cause invasive infections including urosepsis, lymphadenitis, spondylodiscitis and infective endocarditis especially in elderly men with underlying urinary tract diseases.
-
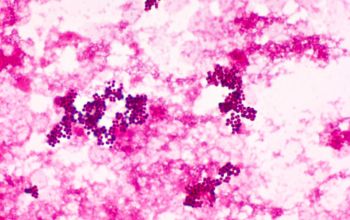
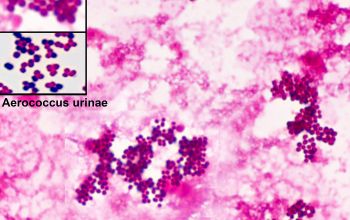
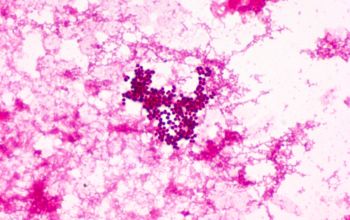
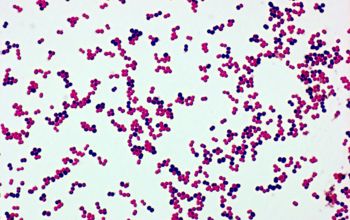
Gram stain
Gram positive cocci,
grouped, in pairs, tetrads, clusters or irregular groups.
-
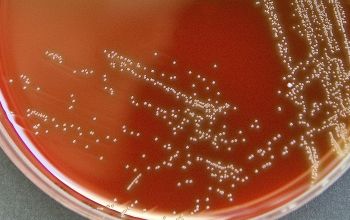
Culture characteristics
-
Facultatively anaerobic
BA: colonies are small (0.5 mm after 24 h), α-hemolytic, convex, shiny, and transparent.
Greening reaction is produced on bloodagar presumably as a result ot H2O2 productions.
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition