Staphylococcus schleiferi
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Staphylococcaceae
Natural habitats
Isolated from the human skin.
Clinical significance
S. schleiferi can be an opportunistic pathogen.
It is associated with a variety of infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and infections in immunocompromised individuals.
Its clinical significance lies in its ability to cause infections, particularly in cases where the immune system is weakened or where medical devices are involved.
Is repeatedly CNS, in pure culture or in mixed culture isolated from the material, then this confirms the presence of an infection.
The correct identification of CNS is necessary in order to get an idea of the pathogens in this group.
-
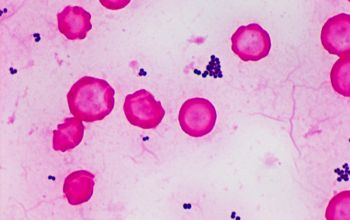
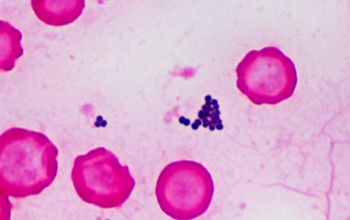
Gram stain
Gram positive cocci,
0.8-1.2 µm
that occur in irregular grape-like clusters and, less often, single and in pairs, tetrads, and in short chains.
-
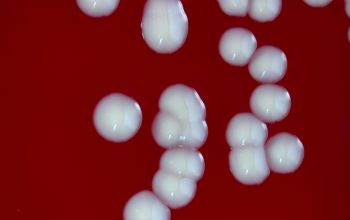
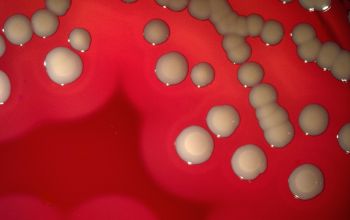
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
BA: medium to large, smooth, glossy, slightly convex, with ß-hemolysis and non pigmented
McConkey: growth
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition