Staphylococcus auricularis
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Staphylococcaceae
Natural habitats
They are ubiquitous in nature, but are mainly found on the skin of human, mammals and birds.
Clinical significance
S. auricularis is part of the healthy human external auditory canal microbiota exclusively colonizing this region
They have a relatively low virulence and can cause infections in patients with lowered resistance, especially in immune compromised patients.
CNS infections occur in implantation of foreign objects, such as intravenous catheters or bone prostheses.
Is repeatedly CNS, in pure culture or in mixed culture isolated from the material, then this confirms the presence of an infection.
The correct identification of CNS is necessary in order to get an idea of the pathogens in this group.
-
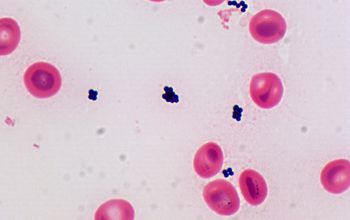
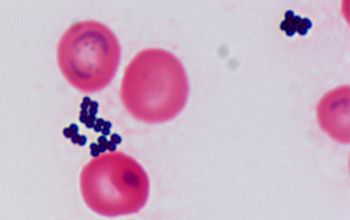
Gram stain
Gram positive cocci,
0.8-1.2 µm
predominantly in tetrads and pairs.
-
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
BA: colonies are small to medium, smooth, butyrous, convex, opaque, circular, slightly glistening, white
and no hemolysis
Some strains can have colonies with a granular texture, wrinkled, or rough surface.
McConkey: growth
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition