Alloiococcus otitidis
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Carnobacteriaceae
Clinical significance
They have been isolateed from human middle ear fluid.
Acute otitis media, persistence of middle ear effusion (MEE) without signs or symptoms of acute infection is recognized in c. 10% of children; this is otitis media with effusion (OME). Chronic OME or the persistence of nonpurulent fluid in the middle ear with minimal constitutional symptoms can lead to significant hearing loss with problems in development of speech, language and the acquisition of social skills
-
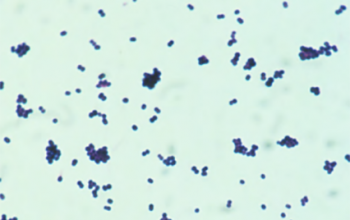
Gram stain
Gram positive ovoid cocci
occuring mostly in pairs and clusters.
-
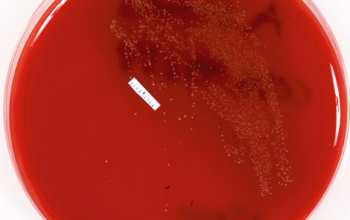
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate aerobic
Isolate can take 4-5 days to appear
BA: they form small alpha-hemolytic colonies after 48 h.
After 7 days of icubation colonies are 1.5 mm
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition
Isolation of Alloiococcus otitidis from Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australian children with chronic otitis media with effusion Christopher Ashhurst-Smith, FEMS Immunology & Medical Microbiology, Volume 51, Issue 1, 1 October 2007, Pages 163–170