Shewanella putrefaciens
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Shewanellaceae
Formerly: Pseudomonas Malitof apathogenic: S. baltica, S. fidelis, S. frigidimarina, S. profunda
Natural habitat:
In the environment and in food products, does not belong to the normal flora of the human being.
- S. algae occurs in the vicinity of salt water
- S. putrefaciens isolated from fish, chicken, meat, fresh and saltwater.
Clinical significans
Clinical significance unknown.
Is often found in mixed cultures. In cellulitis, otitis media, skin and soft tissue infections, peritonitis, respiratory- and urinary tract infections S. algae is most commonly isolated in humans
> 80% (Note errors) and is considered to be more virulent than S. putrefaciens
-
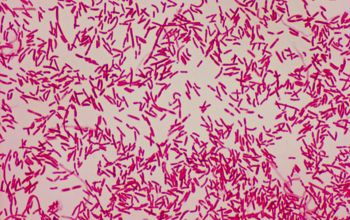
Gram stain
Gram-negative rods.
-
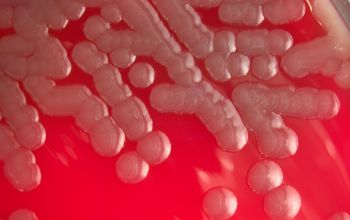
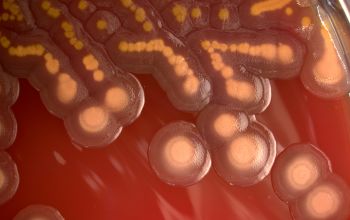
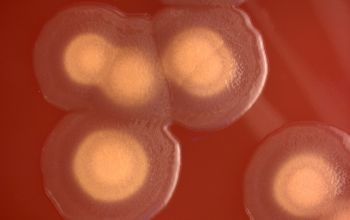
Culture characteristics
-
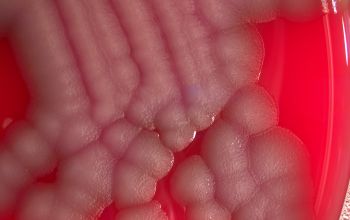
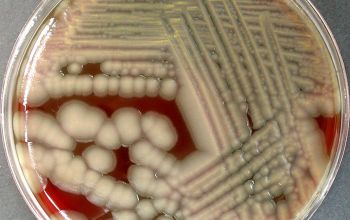
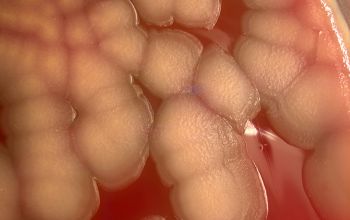
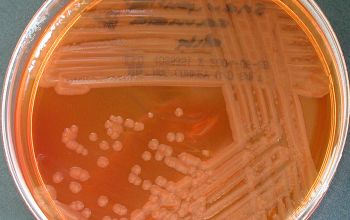
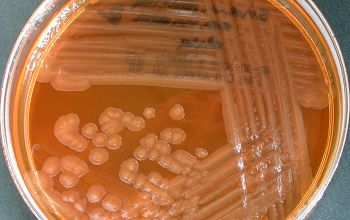
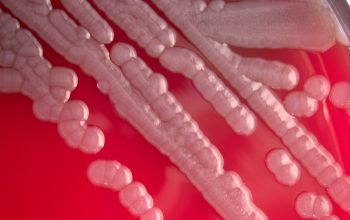
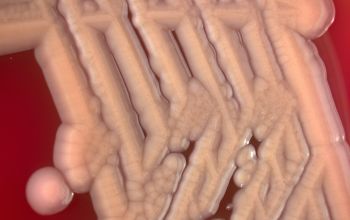
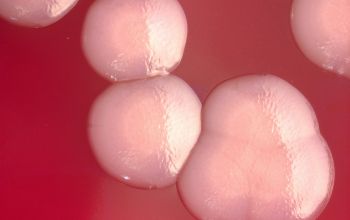
Obligate Aeroob BA: convex, smooth and sometimes mucoid colonies with yellow / brown - brown pigment and give a green discoloration of the bloodagar.
- S. algae is always hemolytic (after 48-72 hours), it can be mucoid
- S. putrefaciens, is usually not- haemolytic and not mucoid
McConkey: growth, non lactose fermenter
BBAØ: no growth
Warning!!!!!! As the two species seem to have different potential for humans, correct identification is important.
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition