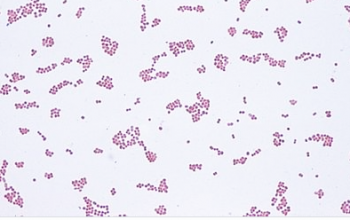
Psychrobacter phenylpyruvicus
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Moraxellaceae
Formily: Moraxella
P. phenylpyruvicus
Natural habitat
They can be isolated from soil, seawater, seabirds especially penguins, fish, poultry,irradiated foods and from human clinical isolates.
It may occasionally be an opportunistic human pathogens.
Clinical significance
Can cause humans infections such asendocarditis, peritonitis, and fungating lesions of the foot, but those infections caused by this bacterium are rare.
BE AWARE that Brucella sp can be MISIDENTIFIED as P. phenylpurivicus or H. influenzae
-
Gram stain
Gram negative coccobacillus
have a tendency to resist decolorization
-
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate Aerobic / fastidious
Grows between 4-35ºC
BA: colonies are smooth, translucent to semi-opaque, small 0.5 mm after 24 hours of incubation,
McConkey: growth,
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition
https://phil.cdc.gov/Details.aspx?pid=12386 photo CDC