Moraxella osloensis
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Moraxellaceae
Natural habitat
They are common inhabitants of the upper respiratory tract
Clinical significance
Usually nonpathogenic and rarely infects humans
They have been reported as rare causative pathogen of infections in humans.
-
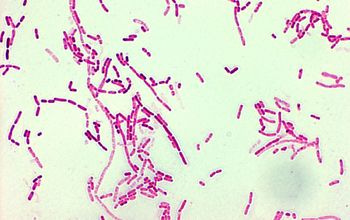
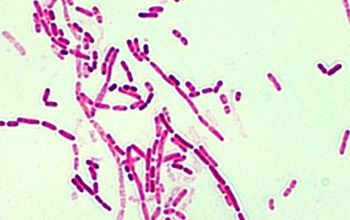
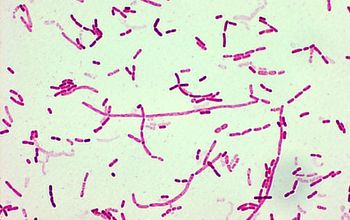
Gram stain
Gram negative plump rods,
1-2 µm,
nearly often square ends,
often very short diplobacilli, occasionally occurring in short chains.
May show variation in size and shape, often with giant forms and filamentous forms, especially in old cultures..
-
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate aerobic
BA: colonies are 1 mm after 24 hours, circular surface, unpigmented, and no corroding in the agar
Non-hemolytic.
Some strains are very mucoid.
McConkey: variable
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition