Chryseobacterium indologenes
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Flavobacteriaceae
Formerly Flavobacterium indologenes,
Apathogen: C.ginsenosidimutans, C.hagamense, C.joostei, C.oranimense, C.scophthalmum
Natural habitat
They are ubiquitous in the environment, in food products, in an aqueous environment of a hospital, such as; the sink, incubators, water from the tap, hemodialysis systems and all kind of aqueous solutions.
They are not a member of the normal human flora.
Clinical significance
Transmission through contaminated equipment or solutions.
Origin is not always known.
Almost never a clinical significance.
Described as a cause of bacteremia in immunocompromised patients or hospital infection through contaminated instruments
and has been identified as the cause of neonatal meningitis.
No transmission from human to human
-
Gram stain
Gram negative rods,
0.5 x 1.0-3.0 µm,
often with convex / rounded ends or else seen, thinner in the middle of the cell.
Filamentous forms also occur.
-
Culture characteristics
-
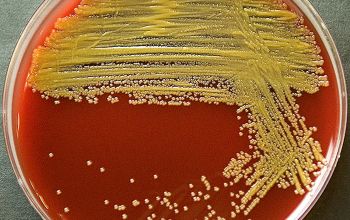
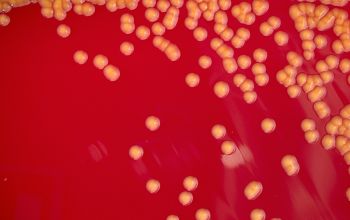
Obligate Aerobic
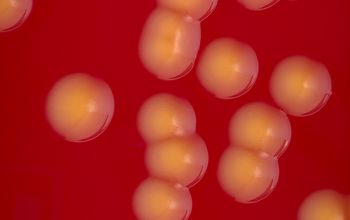
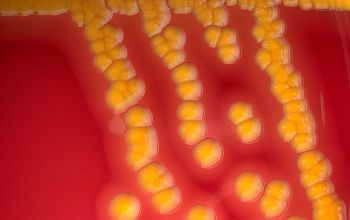
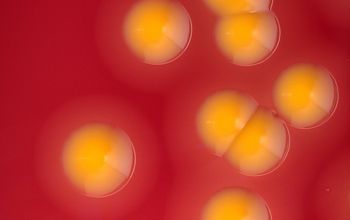
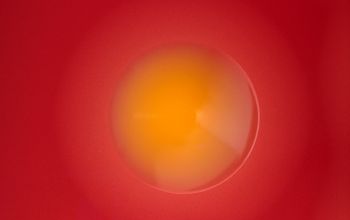
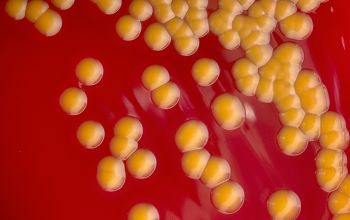
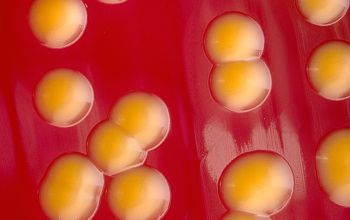
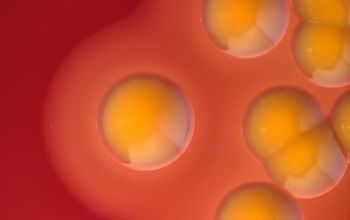
BA: colonies are smooth, low convex and have a dark yellow pigment (flexirubine) within 3 days and a large β-hemolytic zone.
Only C. indologenes is β-hemolytic.
Colonies without pigment also occur
McConkey: growth, non lactose fermenter (66%)
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition