Ralstonia pickettii
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Burkholderiaceae
Formerly Burkholderia
Natural habitat
They are found in moist environments such as soils, on plants, fruits and vegetables.
Because they survive in a moist environment, they can cause problems in a hospital.
Be isolated from CF patients.
Clinical significance
They are rarely found as a cause of infection.
The bacteria has seriously affected humans with poor health.
Several hospitals have reported outbreaks, in particular, patients with cystic fibrosis and Crohn’s Disease have been shown to be infected R. pickettii
They can cause pneumonia, meningitis, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, bacteremia and nosocomial infections.
-
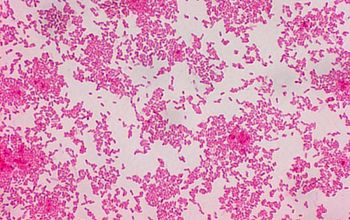
Gram stain
Gram-negative rods.
0.1-0.5 x 1.0-5.0 µm
-
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate Aerobic
BA: grows slowly in primary isolations (> -72 hours), they have no characteristic morphology.
After 24 hours, very small colonies.
Yellow pigment is variable (36%)
McConkey: growth, non lactose fermenter
(McC with salt: 50% growth)
BBAØ: no growth
Warning:
Phenotypically R. pickettii is easily confused with members of the group Pseudomonas fluorescens, and the Burkholderia cepacia complex.
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition