Pseudomonas luteola
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Pseudomonadaceae
Formerly: Chryseomonas
Natural habitat
Is an oppertunistic pathogen, found ubiquitously in damp enviroments.
Clinical significance
P. luteola is a rare cause of infections in humans.
There have been case reports of a variety of different infections, including bacteremia, cellulitis, osteomyelitis, peritonitis, endocarditis, and postsurgical meningitis.
Also infections in patients with underlying diseases or in association with foreign body.
-
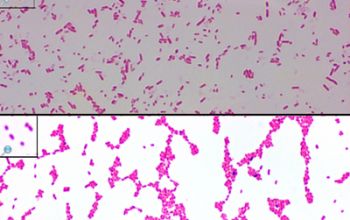
Gram stain
Gram negative rods,
0.8 x 2.5 µm
-
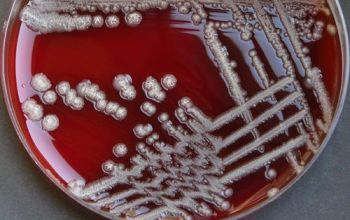
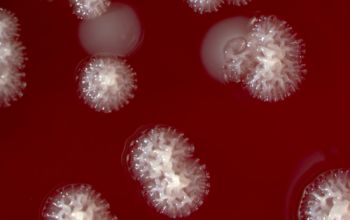
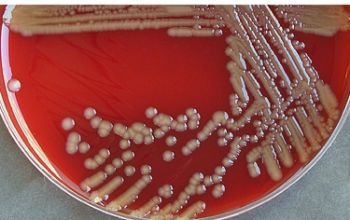
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate Aerobic
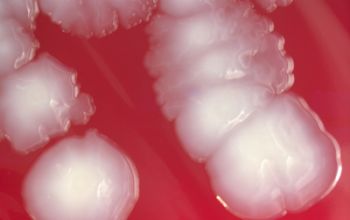
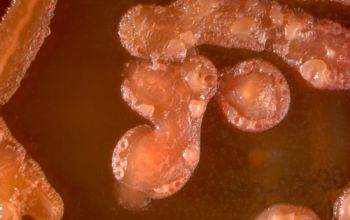
BA: they typically exhibit rough, dry, wrinkled, adherent, non-hemolytic colonies or, more rarely, smooth colonies.
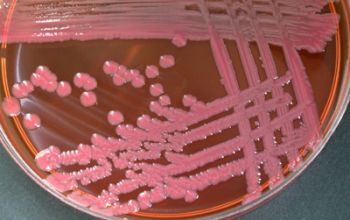
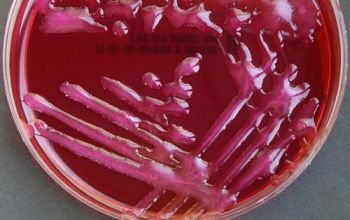
McConkey: growth, non lactose fermenter
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition