Capnocytophaga gingivalis
-
General information
Taxonomy Family: Flavobacteriaceae, genus: C.ochracea, C.gingivalis, C.sputigena, C.haemolytica and C.granulosa
Natural Habitat They are normal inhabitants of the human mouth
Clinical Significance The first three are also associated with juvenile and adult periodontitis, whereas the latter two been isolated from supragingival plaque of healthy adults as well as from subgingival plaque in adult periodontitis.
All five species may cause septicemia and other infections in immunosuppressed (mainly neutrpenic) patients.
-
Gram stain
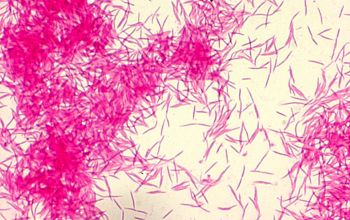
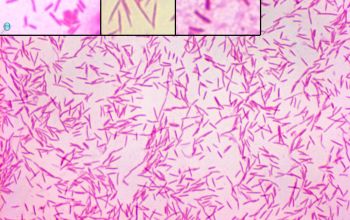
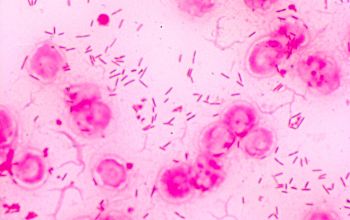
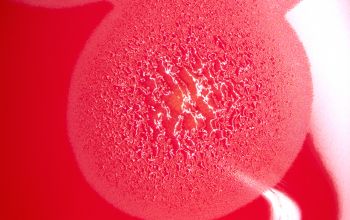
Gram negative rods. They are mainly fusiform, medium to long cells with tapered ends. Sometimes filamentous forms. In older cultures, they can be pleomorphic, with swollen or large coccoid cells. Size: 0.4-0.6 x 2.5-7.5 µm
Wet mount slide
Cultures that are in the log phase one sees a "sliding / floating" movement.
-
Culture characteristics
-
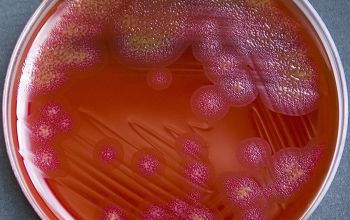
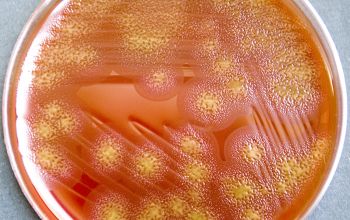
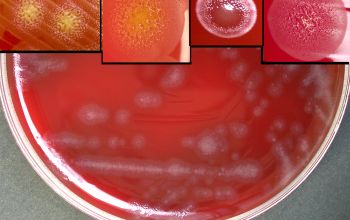
Facultative anaerobic 5% CO2 improves the growth BA: colonies are convex or flat and often slihtly yellow when scraped of agar, show regular or spreading edges and adhere to the agar surface. They are not hemolytic
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition