Pantoea agglomerans
-
General information
was: Enterobacter agglomerans
P. agglomerans
P. dispersa (rarely)
Pathogeen voor planten
P. ananatis, P. stewartii ssp indologenes, P. stewartii ssp stewartii, P. terrae
Natural habitats
Widely distributed in nature. Isolated from human and animals stools
Clinical significance P. agglomerans can cause opportunistic infections in immune compromised patients.
-
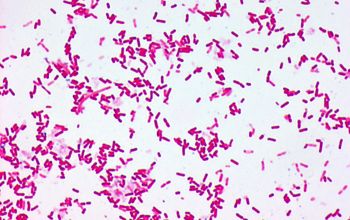
Gram stain
Gram negative rods,
0.5-1.3 x 1.0-3.0 µm
-
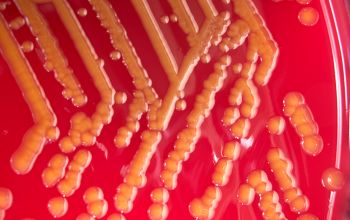
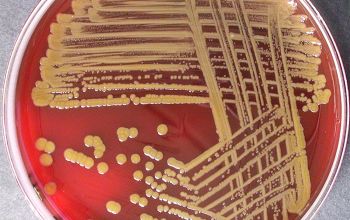
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
BA: colonies are smooth, translucent, low convex, with entire marges.
Nonpigmented or yellow (75%), pale beige to pale reddish yellow colonies.
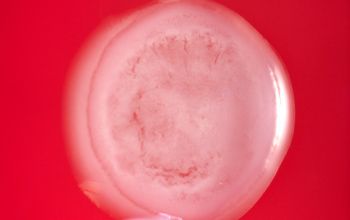
McConkey: growth
Lactose Fermenter and Non Lactose Fermenter
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition