Enterobacter cloacae
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Enterobacteriaceae
E. aerogenes
E. cloacae complex
- E. cloacae, E. asburiae, E. hormaechei, E. kobei, E. ludwigii
E. amnigenus I
E. cancerogenus
E. gergoviae
E. intermedium
Pathogenic to plants: E. amnigenusII, E. cowanii, E. pyrinus, E. radicincitans
Natural habitats
Can be found in soil, water, sewage, food and also on the human skin and in the intestinal tract.
Clinical significance
Enterobacter species cause a wide variety of nosocomial infections, including respiratory- and urinary tract infections, wound infections, osteomyelitis, meningitis and bacteremia.
Especially patients which are hospitalized for more than 72 hours and immunocompromised patients are at risk for an infection caused by Enterobacter.
-
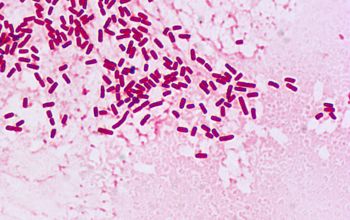
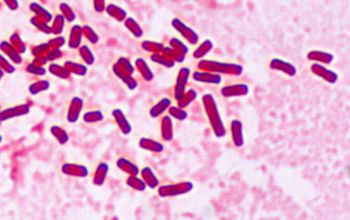
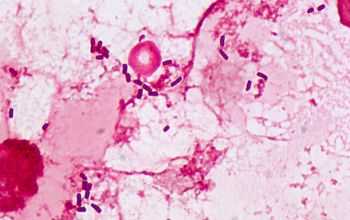
Gram stain
Gram negative straight rods,
0.6-1.0 x 2-3 µm,
found singly or in pairs.
Some encapsulated
-
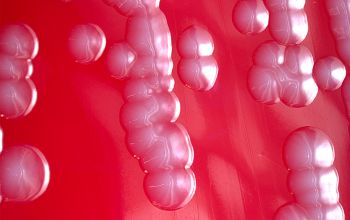
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
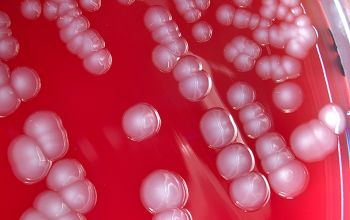
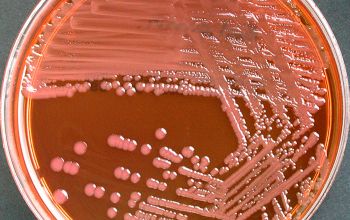
BA: colonies are large 2-3 mm, gray, smooth, shiny and sometimes flat with irregular edges, they can also be mucoid (strains with K-antigen have a capsule)
They are nonpigmented.
McConkey: growth, lactose fermenter
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition