Cronobacter sakazakii
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Enterobacteriaceae
Formerly known as Enterobacter sakazakii
Natural habitats
Can be found in soil, water, sewage, food, some dairy products and also on the human skin and in the intestinal tract.
Cronobacter sakazakii have also been found in powdered baby food.
The bacterium can grow at a low temperature, growth at 8 ° C has been documented.
Clinical significance
May cause significant infections in various anatomical sites.
Meningitis, necrotizing enterocolitis and sepsis associated with high mortality have been documented in especially neonates.
-
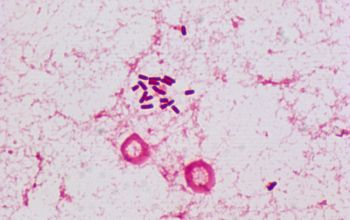
Gram stain
Gram negative straight rods,
0.6-1.0 x 1.2.0-3.0 µm,
found singly or in pairs.
Some encapsulated
-
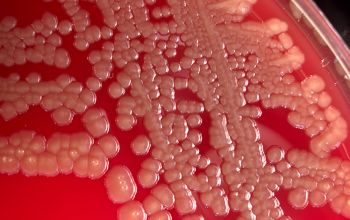
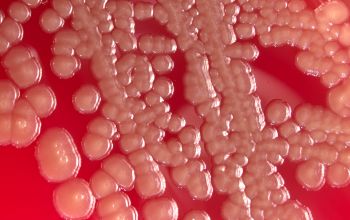
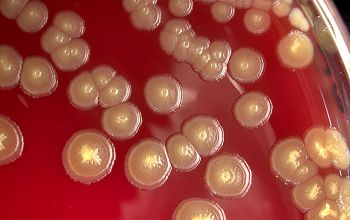
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
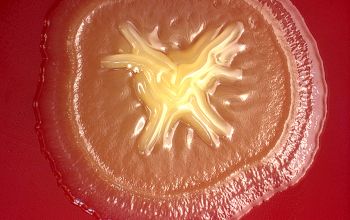
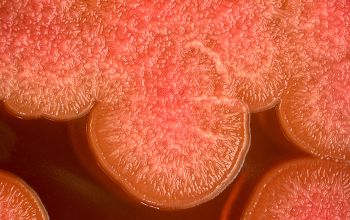
BA: colonies are pale yellow (bright yellow at room temperature) 1-3 mm.
Colonies are often winded in the center with a star-like appearance.
McConkey: growth lactose fermenter
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition