Neisseria subflava
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Neisseriaceae
This species contains the former species N. subflava, N. perflava, and N. flava
Natural habitats
N. subflava is a common commensal of the human oropharynx.
Clinical significance
Has occasionally been associated with invasive diseases such as meningitis, endocarditis, and bacteremia.
-
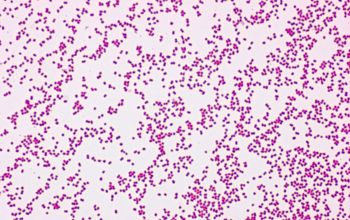
Gram stain
Gram negative diplococci,
appears in pairs
-
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate aerobic
5% CO2 improves the growth
N. subflava may produce a yellowish pigment
BA: colonies are smooth and are variably transparent with a yellowish pigment.
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition