Neisseria sicca
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Neisseriaceae
Natural habitats
Most human Neisseria spp are considered normal inhabitants of the upper respiratory tract.
Clinical significance
It can appear as an opportunistic pathogen.
N. sicca was implicated, e.g., the causitive agent of endocarditis.
-
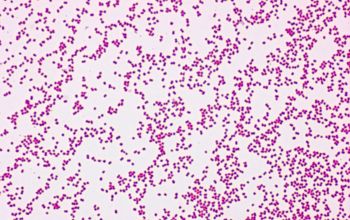
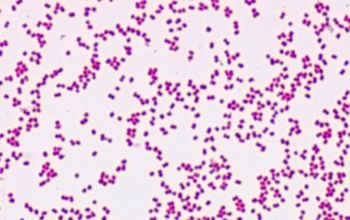
Gram stain
Gram negative diplococci,
appears in pairs
While Neisseria species are gram negative, occasionally a tendency to withstand decolorization.
-
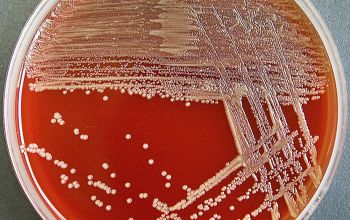
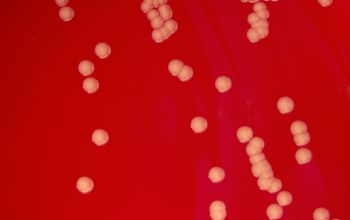
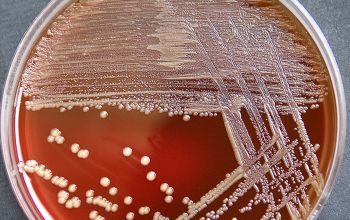
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate aerobic
5% CO2 improves the growth
BA: they may produce a yellowish pigment
The colonies are large, ≤ 3 mm, smooth, with entire edges and can form dry, wrinkled, and grayish white, although some strains may produce a yellow pigment.
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition