Clostridium difficile
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Clostridiaceae
Natural habitats
They inhabits the microflora of intestines of humans. Around 3% of healthy adults and up to 70% of babies have a number of C. difficile bacteria living in their gut.
However, the number of C. difficile bacteria is kept very low and in control by the millions of harmless bacteria in the intestines that aid in digestion.
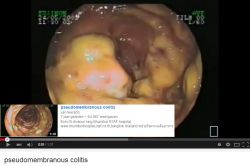
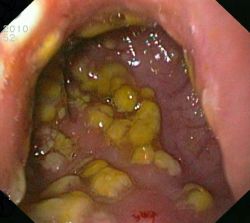
Clinical significance
Is the major cause of antibiotic associated pseudomembranous colitis, is it also the most frequently identified cause of hospital acquired diarrhea.
-
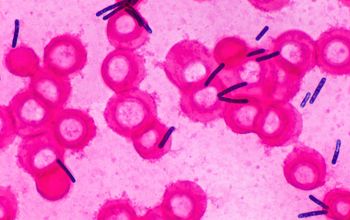
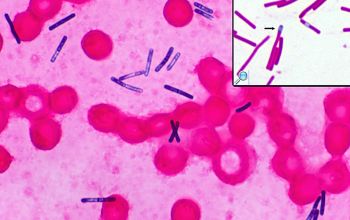
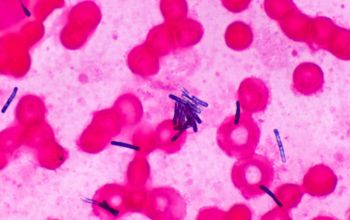
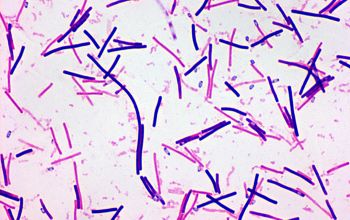
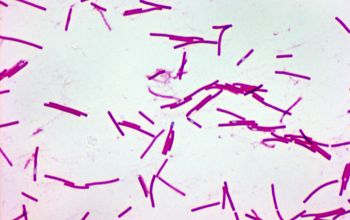
Gram stain
Gram positive to Gram variable rods,
0.5-0.9 x 3.0-5.0 µm.
Spores oval / subterminal or terminal / free spores
Swelling of the cell negative
-
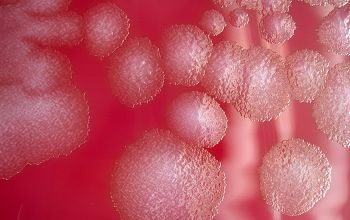
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate anaerobic
BBAØ: colonies are 2-5 mm, creamy yellow to gray-white, irregular, coarse, mottled to mosaic internal structure, matt to glossy surface.
Nonhemolytic.
Fluorescence: pale green
Odor: horse stable
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition