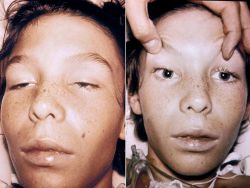
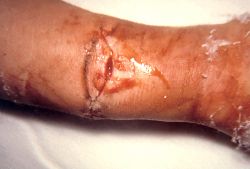
Five days after sustaining a compound fracture of his right arm, this 14-year-old boy noticed that he had blurred vision. Four days later, he could not swallow, move his lips, or protrude his tongue. Other findings included bilateral total ophthalmoplegia with ptosis (left) and dilated, fixed pupils (right). When symmetric, descending cranial nerve paralysis develops four to 14 days after an open injury and spares mental and sensory function, think of wound botulism.
Author Herbert L. Fred wikimedia commons
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Botulism1and2.JPG
Clostridium botulinum
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Clostridiaceae
Natural habitats
Spores are widely distributed in soil and aquatic habitats
Clinical significance
They are the cause of the rare but frequently fatal illness known as botulism and which is characterized by weakness, trouble seeing, trouble speaking and flaccid paralysis.
Botulism
Occur in a few different ways.
Foodborne botulism, happens when food containing the toxin is eaten.
Infant botulism, happens when the bacteria develops in the testiness and releases toxin.
This only happens in children less than 6 months of age as after that protective mechanisms develop.
Wound botulism is found most often among those who inject street drugs
It is not passed directly between people.
-
Diseases
-
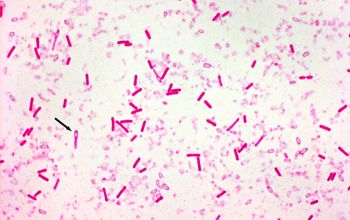
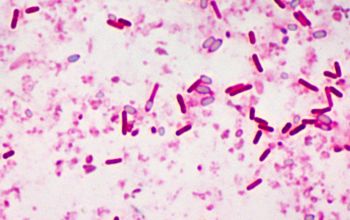
Gram stain
Gram positive rods,
0.6-2.4 x 1.6-22.0 µm,
which are often negatively stained, and free spores
Spores oval / subterminal
Swelling of the cell positive
-
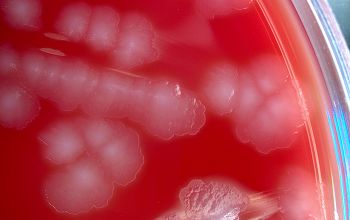
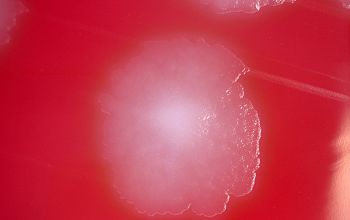
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate anaerobic
BBAØ: 4 types of colony morphologies
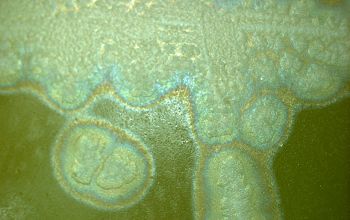
Colonies are 2-6 mm, β-hemolytic (variable), flat to raised, translucent to semi opaque, gray, circular to irregular, scalloped or rhizoid margin, often with a mottled or crystalline internal structure.
-
-
Characteristics
- Gram-positive
- bacilli
- large-bacilli
- spores
- growth obligate-anaerobic
- catalase-negative
- oxidase-negative
- indole-negative
- urease-negative
- lecithinase-negative
- motility
- vancomycin-susceptible
- colistine-resistant
- beta hemolysis-variable
- smell-rotten eggs
- lipase-positive
- motility-peritrichous flagella (most)
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition