Clostridium tertium
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Clostridiaceae
Natural habitats
Found in soil and gut of humans and other animals
Clinical significance.
Is considered to be a weak pathogen, but it has been implicated in severe infections, and has been increasingly recognized as a cause of bacteremia and other infections in immunocompromised patients, especially those with hematologic malignancies.
-
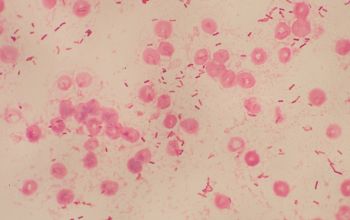
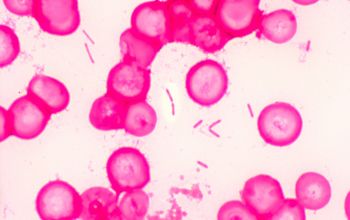
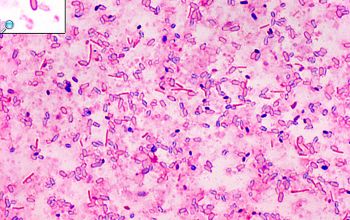
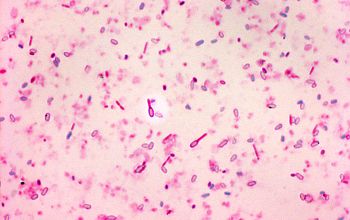
Gram stain
Gram positive straight rods (Gram negative stained),
0.5-1.4 x 1.5-10.2 µm,
occurring singly or in pairs
Only forms spores under anaerobic conditions
Spores oval / terminal
Swelling of the cell positive
-
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate anaerobic ►AEROTOLERANT
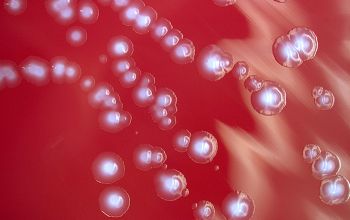
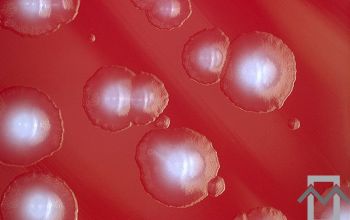
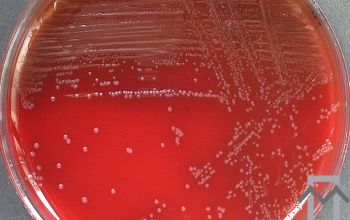
BBAØ: colonies are 2-4 mm in diameter, circular, low convex, have slightly irregular margins, are white to gray and have a matt surface and usually a mottled or granular internal structure.
Hemolysis is variable and when present, colonies may be alpha- or beta-hemolytic.
BA (aeroob) growth: colonies are 1 mm, circular with entire edges, are dome shaped and have an opalescent appearances.
Colonies in agar are small and lenticular
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition