Bifidobacterium species
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Bifidobateriaceae
Before the 1960s, Bifidobacterium species were collectively referred to as "Lactobacillus bifidus"
Natural habitats
They belong to the normal flora of the gut and oral cavity.
Some bifidobacteria are used as probiotics.
Clinical significance
Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli play an important role in the development of the healthy gut and its associated immune defenses.
Because of this, they are generally considered to be non-pathogenic but nevertheless are isolated from infections of polymicrobial etiology.
Dental caries is the most common clinical entity in which Bifidobacterium, mainly B. dentium.
-
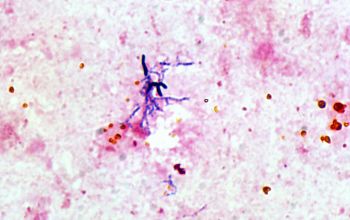
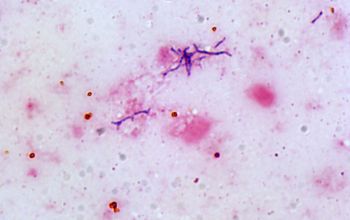
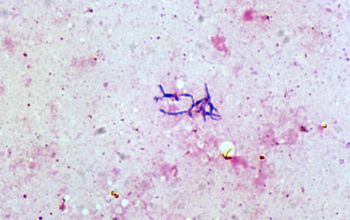
Gram stain
Gram-positive rods, the cells often stain irregular.
Non-acid-fast.
Pleomorphic, coryneform rods. they usually appear clubbed or branching and may display bifurcated ends.
Some species occasionally exhibbit swollen coccoid foms.
Size 0.5-1.3 by 1.5-8.0.µm.
Bifidobacterium spp are sometimes arranged in pairs, "V" arrangements, in chains, and in pallisades of parallel cells or rosettes.
-
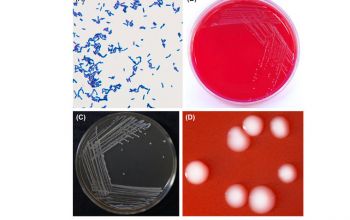
Culture characteristics
-
They are strictly anaerobic or occasionally microaerobic.
They are nutritionally fastidious
BA: produces a white, convex, shiny colony with irregular eges in solid media.
BBAØ: growth
Growth in broth is diffuse
-
-
Characteristics
-
References