Prevotella corporis
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Prevotellaceae
Natural habitats
Belong to the normal flora of the oropharynx, gastrointestinal tract, the genitals and urinary tract.
Clinical significance
Prevotella species are among the dominating microorganisms of the oral cavity, where they, despite their commensalism, can be involved in nearly all types of oral infections.
Some are important pathogens in bite wounds and infections of the head, mouth, neck and lungs and they are typical polymicrobial infections.
-
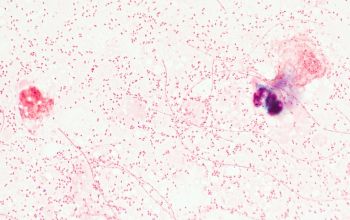
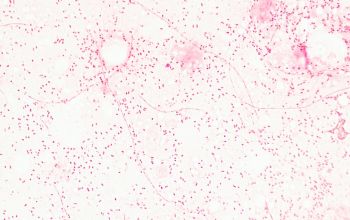
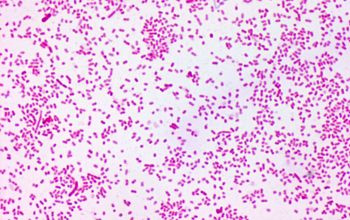
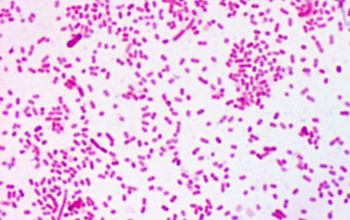
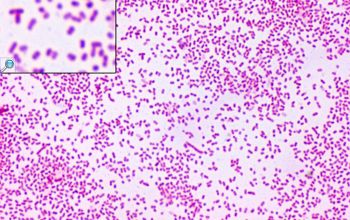
Gram stain
Gram negative coccobacilli or bacilli,
evenly colored with rounded ends, which often occur in pairs or short chains.
Liquid medium
the bacteria can be more polymorphic, longer and have vacuoles
-
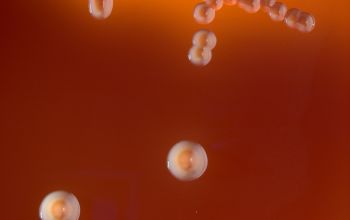
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate anaerobic
BBAØ: this pigmented group is growing more slowly than the Bacteroides sp and take for the formation of pigment 2 days to 3 weeks, they are often hemolytic.
P. corporis have dry colonies
BBEØ: no growth
KVBAØ: (BA with kanamycin and vancomycin)
colonies are black
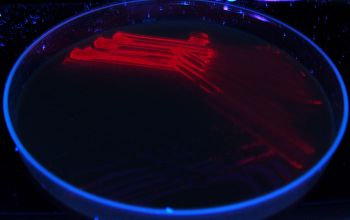
Fluorescentie/woods lamp: brick red (that appears before the brown pigment
Older cultures in which the black pigment has become visible, do not fluoresce.
The fluorescence of Prevotella is also directly in wound fluid or pus visible.
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition