Corynebacterium mucifaciens
-
General information
The pathogenic potential of coryneform bacteria has been underestimated
Taxonomy
Family: Corynebacteriaceae
Natural habitats
Part of the normal flora of skin, their potential pathogenicity still remains to be assessed.
They has been mainly isolated from skin, blood and from normally sterile body fluids
Clinical significance
C. mucifaciens should be considered as important human pathogen in patients with severe illness and compatible history of exposure even in individuals with no clearly identified immunosuppression.
C. mucifaciens has mainly been isolated from blood cultures and other sterile body fluids, but it has also been recovered from abscesses, soft tissue, dialysates, and cavitary pneumonia, as welkl as ear and nasaopharynx.
Corynebacterium species are becoming recognized as an increasing cause of opportunistic infections.
-
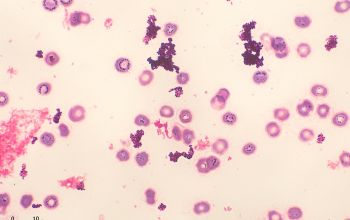
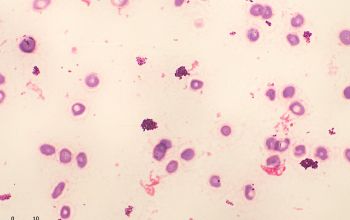
Gram stain
Gram positive rods,
irregularly shaped (‘coryneforms”), they are arranged as single cells, in pairs, in V forms, in palisades, or in clusters with
a so-called Chinese-letter appearance.
Club-shaped rods are observed in true members of the genus Corynebacterium only
-
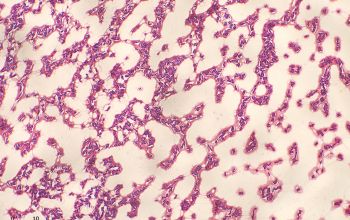
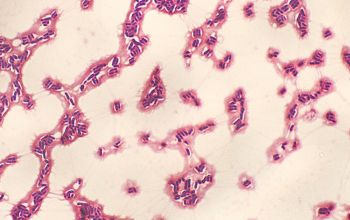
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate aerobic
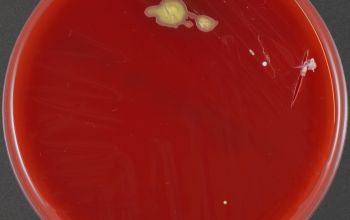
BA: colonies are very distict because they are slightly to overtly yellow and very mucoid.
(very few strains are not mucoid)
Colonies are about 1 to 1.5 mm after 24h of incubation and have entire edges.
They appear less mucoid after extended incubation for 96h.
C. mucifaciens exhibiting such mucoid colonies, this characteristic strongly reminds bacteriologists of Rhodococcus equi colonies.
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition
Corynebacterium mucifaciensin an immunocompetent patient with cavitary pneumonia Félix Djossou, BMC Infectious Diseases201010:355