Corynebacterium striatum
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Corynebacteriaceae
Natural habitats
They occur in the normal flora on both skin and oropharynx.
Clinical significans
Corynebacterium striatum is an emerging opportunistic pathogen, especially important in hospital settings.
Key points
- Part of the normal skin and mucosal flora
- Increasingly recognized as a true pathogen, not just a contaminant, when isolated from sterile sites
Clinically relevant infections
- Bacteremia / sepsis
- Endocarditis
- Pneumonia (especially ventilator-associated)
- Wound and surgical site infections
- Catheter- and device-related infections
- Osteomyelitis (reported)
Risk factors
- Immunocompromised patients
- Prolonged hospitalization or ICU stay
- Indwelling medical devices (central lines, prostheses)
- Prior broad-spectrum antibiotic use
Antibiotic considerations
- Frequently multidrug-resistant
- Often resistant to β-lactams, macrolides, and fluoroquinolones
- Vancomycin is usually the drug of choice (until susceptibility results are available)
Clinical importance
- Should be considered clinically significant when recovered from sterile sites
- Requires targeted therapy, not dismissal as a contaminant
-
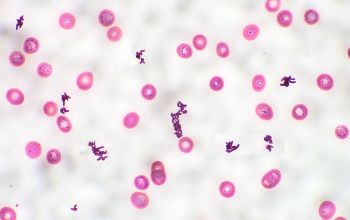
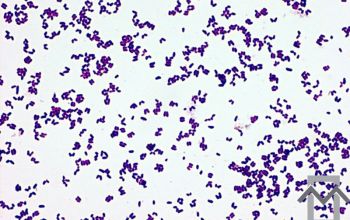
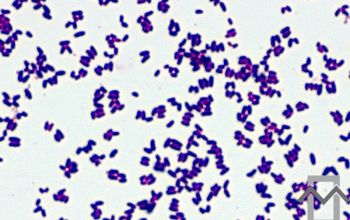
Gram stain
Gram positive rods,
irregularly shaped (‘coryneforms”), they are arranged as single cells, in pairs, in V forms, in palisades, or in clusters with
a so-called Chinese-letter appearance.
Club-shaped rods are observed in true members of the genus Corynebacterium only
-
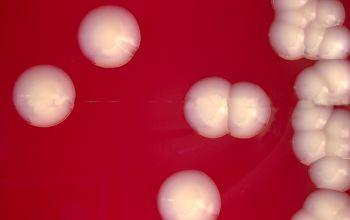
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
BA: colonies are convex, circular, shiny, moist, and creamy, and about 1 to 1.5 mm after 24 hours of incubation.
(somewhat like coagulase-negative-staphylococci (CNS))
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition
Clinical Microbiology of Coryneform Bacteria Guido Funke Clin Microbiol Reviews, jan 1997