Kocuria kristinae (Rothia kristinae)
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Micrococcaceae
Genus: Rothia kristinae
Formely: Kocuria kristinae
Natural habitats
Micrococci are widespread in nature and are commonly found on the skin of humans and other mammals.
Clinical significance
They thought of as harmless or commensal organism, though it can be an opportunistic pathogen, there have been rare cases of infections in people with compromised immune systems.
-
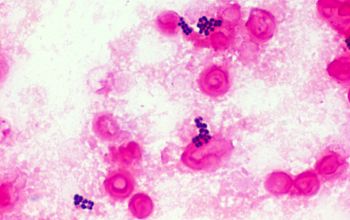
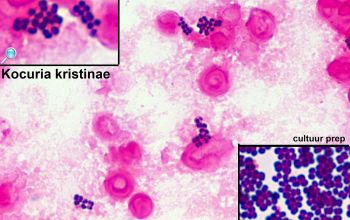
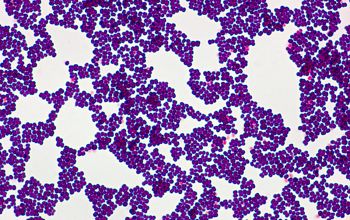
Gram stain
Gram positive cocci,
0.5-3.5 µm,
occurring mostly tetrads, and irregular clusters.
Mature cells lose the ability to retain the crystal violet, which makes them decolorization easier than younger cells.
-
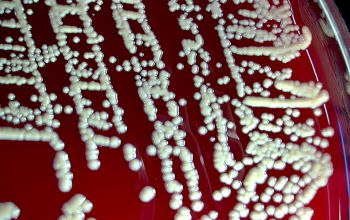
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate aerobic
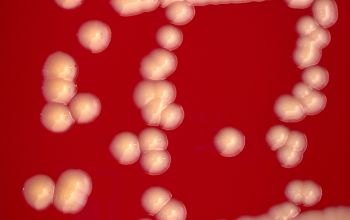
BA: after 48 hours the colonies are 1-2 mm in diameter (grow more slowly than staphylococci).
Colonies dull or matte, convex and have a pale orange pigment
McConkey: growth
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition