Pseudomonas oryzihabitans
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Pseudomonadaceae
Genus: formerly Flavimonas
Natural habitat
Isolated from soil, water, plants and clinical specimens.
Does not belong to the human flora.
Clinical significance
Has only rarely been associated with human infections.
Infections is frequently linked to implanted or indwelling materials or to invasive procedures.
-
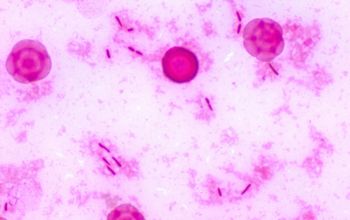
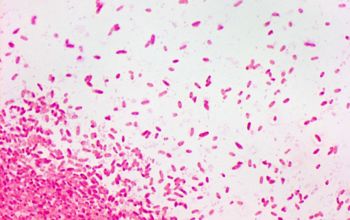
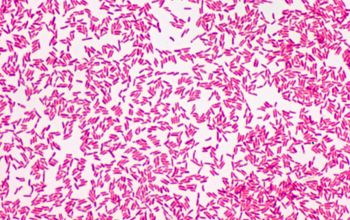
Gram stain
Gram negative rods,
0.5-0.8 x 1.5-3 µm
-
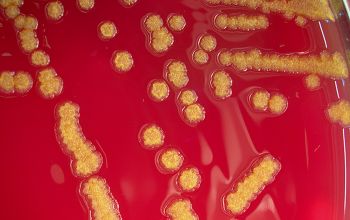
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate Aerobic
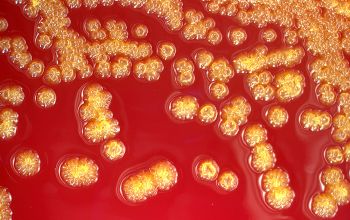
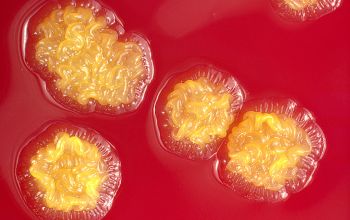
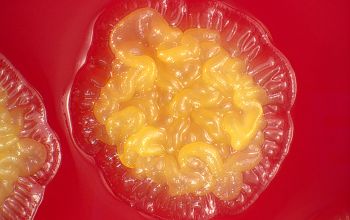
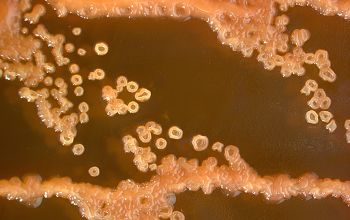
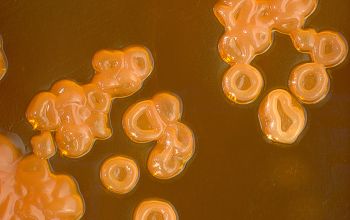
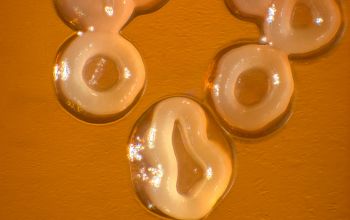
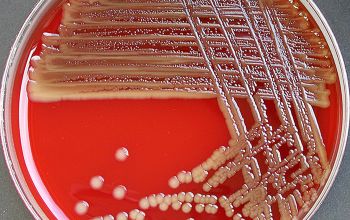
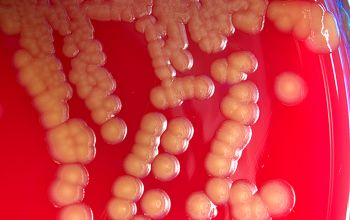
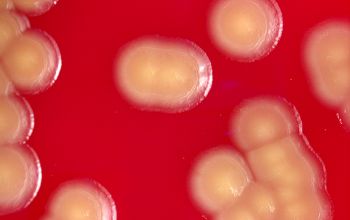
BA: they typically exhibit rough, dry, wrinkled, adherent, non-hemolytic colonies or, more rarely, smooth colonies.
Both have a yellow pigment.
McConkey: growth, non lactose fermenter
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition