Clostridium sordellii (Paraclostridium sordellii)
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Clostridiaceae
Genus: Paraclostridium sordellii
Formely: Clostridium sordellii
Natural habitats
Ubiquitous in nature
Clinical significance.
Is capable of causing pneumonia, endocarditis, arthritis, peritonitis and myonecrosis, bacteremia and sepsis occur rarely.
Most cases of sepsis from C. sordellii occur in patients with underlying conditions.
Severe toxic shock syndrome among previously healthy persons has been described in a small number of C. sordellii cases, most often associated with gynecologic infections in women and infections of the umbilical stump in newborns.
It has also been described in post-partum females, medically induced abortions, injection drug users and trauma cases.
-
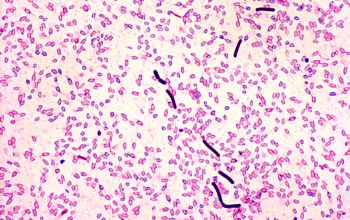
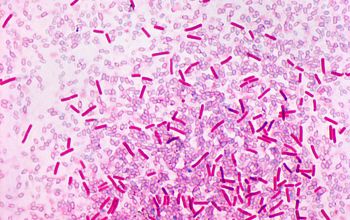
Gram stain
Gram positive, straight rods,
0.5-1.7 x 1.6-20.6 µm,
many free spores, occurring singly or in pairs.
Spores oval / central or subterminal
Swelling of the cell positive (slightly)
-
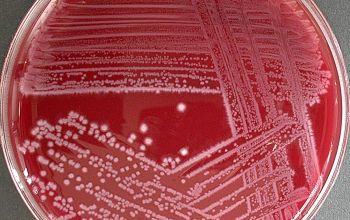
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate anaerobic
BBAØ: colonies are 1-4 mm in diameter, circular to irregular, flat or raised, translucent or opaque, gray or chalk-white, with a dull or shiny surface, a granular or mottled internal structure and a scalloped, lobate or entire margin;
hemolyse is variable
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition