Moraxella catarrhalis
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Moraxellaceae
Natural habitats
Part of the normal flora of the upper respiratory tract, and sometimes colonize the female genitals.
Clinical significance
M. catarrhalis is an exclusively human pathogen and is common cause of otitis media in infants and children and they are an important cause of lower respiratory tract infections, particularly in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
They can cause a variety of severe infections, including pneumonia, endocarditis, septicemia and meningitis,
-
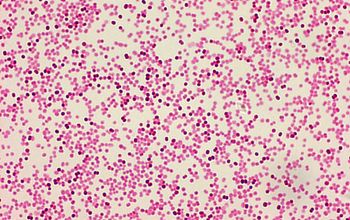
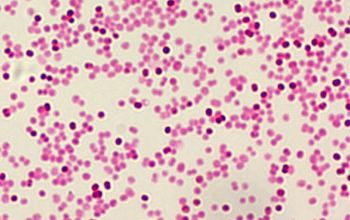
Gram stain
Gram negative diplococci
They occur intra- or extracellularly
-
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate aerobic
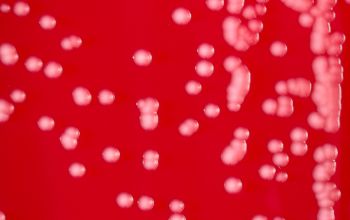
BA: colonies are 1-3 mm after 24 hours, gray to white, opaque, and smooth
When they are pushed by a loop (öse), they remain intact and glide over the agar as a “hockey puck”
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition