Micrococcus luteus
-
General information
Micrococcus was discovered by Sir Alexander Fleming before he discovered penicillin 1928
Taxonomy
Family: Micrococcaceae
Natural habitats Micrococci are widespread in nature and are commonly found on the skin of humans and other mammals.
They are generally believed to be temporary residents and are most frequently found on the exposed skin of the face, arms, hands, and legs.
Clinical significance
M. luteus is typically non-pathogenic and part of the normal flora of the skin and mucous membranes.
However, in immunocompromised individuals, it can act as an opportunistic pathogen and cause infections, although such occurrences are relatively rare.
It has been implicated in conditions like wound infections, urinary tract infections, and, in some cases, endocarditis, especially in people with prosthetic heart valves or other implanted medical devices. In general, M. luteus infections are not as common or severe as infections caused by other bacteria, but they can still pose a risk in vulnerable patients.
The bacterium can also show resistance to certain antibiotics, making treatment more challenging when infections do occur.
-
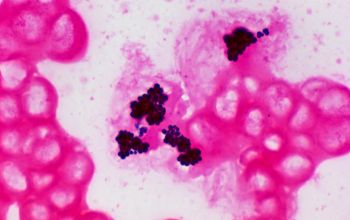
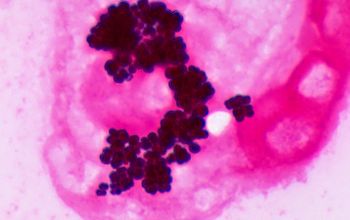
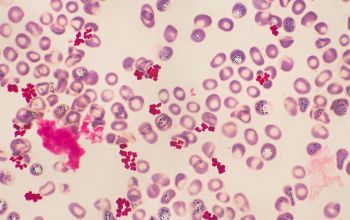
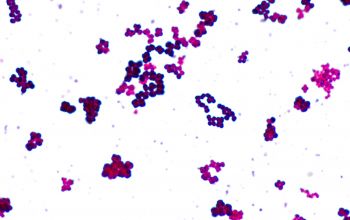
Gram stain
Gram positive cocci,
0.5-1.8 µm,
occurring mostly tetrads, and irregular clusters.
Mature cells lose the ability to retain the crystal violet, which makes them decolorization easier than younger cells.
-
Culture characteristics
-
Obligate aerobic
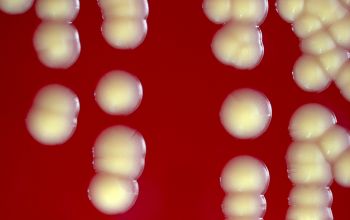
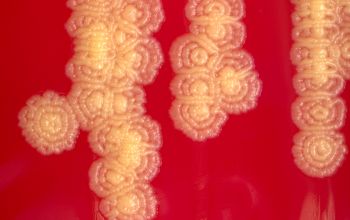
BA: after 48 hours the colonies are 1-2 mm in diameter (grow more slowly than staphylococci).
Colonies dull or matte, convex and bright yellow, and a small percentage are crème-white.
McConkey: growth
BBAØ: no growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition