Streptococcus gordonii
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Streptococcaceae
Streptococcus sanguinis group / Lancefield Group F
- S. sanguinis
- S. parasanguinis
- S. gordonii
Natural habitats
Commensals of the oral cavity, the gastrointestinal tract, and the female genital tract.
Clinical significance
Isolation of these species from blood cultures in asymptomatic patients often does not require antibiotic treatment, if it is due to a transient bacteremia.
They can also be found as transient microbiota of the normal skin and often represent contaminants when isolated from blood cultures.
At the same time these species are the most frequently isolated bacteria in bacterial endocarditis in native valve and less frequently, in prosthetic valve infections.
Careful evaluation of the clinical situation is therefore crucial to correctly interpret the clinical significance of blood culture isolates from the S. mitis- or S. sanguinis group.
In neutropenic patients, streptococcal species from these groups are often responsible for life-threatening sepsis an pneumonia cases following immunosuppression by chemotherapy.
-
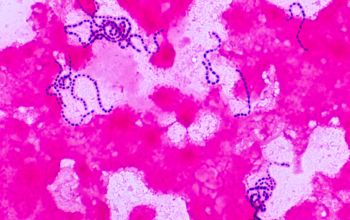
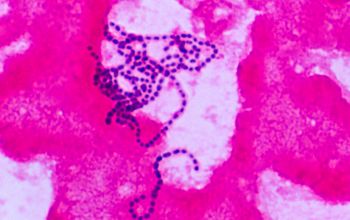
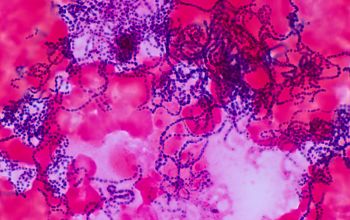
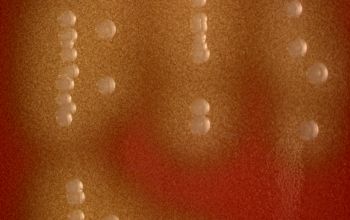
Gram stain
Gram positive streptococci,
grouped in chains
Liquid medium,
they are found in the form of chains of different lengths.
They namely divide into one direction
-
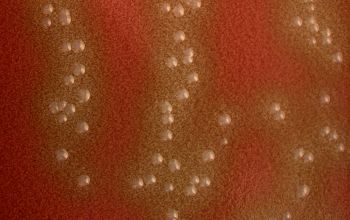
Culture characteristics
-
Facultative anaerobic
5% CO2 improves the growth
BA: are small-colony-forming and α-hemolytic bacteria (< 0.5 mm)
McConkey: no growth
BBAØ: growth (better)
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition