Staphylococcus intermedius
-
General information
Taxonomy
Family: Staphylococcaceae
Natural habitats
They are part of the normal skin and oral flora of dogs and many other animals.
It is a very rare human pathogen.
Most cases are associated with exposure to animals, mostly dogs.
However, they can cause infection in healthy individuals even without exposure to animals.
Clinical significance
They have a relatively low virulence and can cause infections in patients with lowered resistance, especially in immune compromised patients.
CNS infections occur in implantation of foreign objects, such as intravenous catheters or bone prostheses.
Is repeatedly CNS, in pure culture or in mixed culture isolated from the material, then this confirms the presence of an infection.
The correct identification of CNS is necessary in order to get an idea of the pathogens in this group.
-
Gram stain
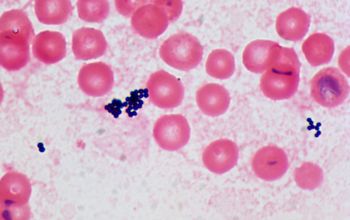
Gram positive cocci,
1.0-1.5 µm
that occur in irregular grape-like clusters and, less often, single and in pairs, tetrads, and in short chains.
-
Culture characteristics
-
S. intermedius maybe misclassified as S. aureus
Facultative anaerobic
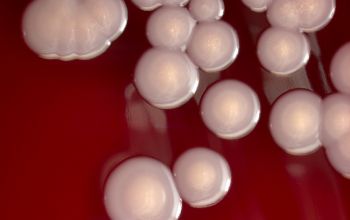
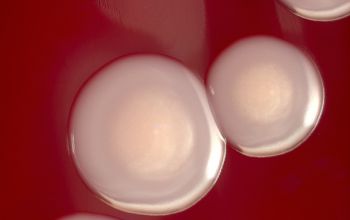
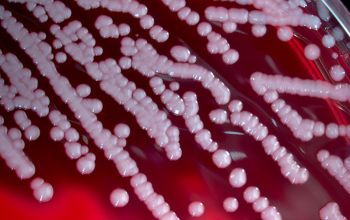
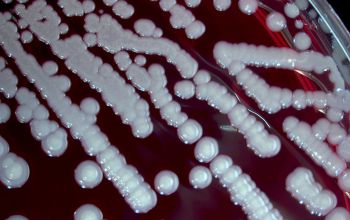
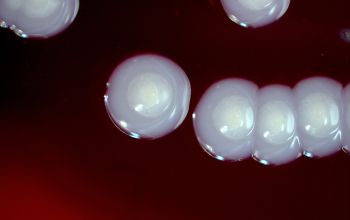
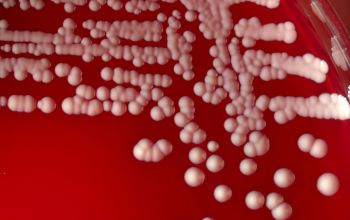
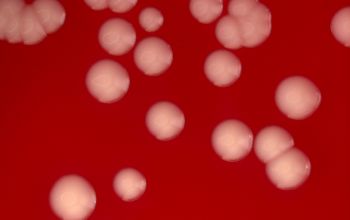
BA: large, entire, smooth, glossy, translucent, slightly convex, β-hemolytic and usually non pigmented
They can give a double hemolysis zone on blood agar
(clear narrow inner zone and a broad turbid outer zone)
McConkey: growth
BBAØ: growth
-
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition









-350x220.jpg)
-350x220.jpg)