Pseudomonas aeruginosa
-
General information
the following information is not yet verified
Taxonomy
Family: Pseudomonadaceae
Natural habitat
Widely distributed in nature. Isolated from soil, water, plants and clinical human specimens.
It is also found in most man-made environments throughout the world.
Because they survive in a moist environment, they can cause problems in a hospital.
Pseudomonas found in all types of aqueous solutions, including disinfectants, soap, eye drops, dialysis fluid, sink etc
Clinical significance
Is the most important pathogen of the genus Pseudomonas.
They cause a broad spectrum of infections, ranging from superficial skin lesions to sepsis.
Infections occur mainly in patients with burns, cystic fibrosis, acute leukemia, organ transplants, otitis externa ("swimmer 's ear") and intravenous drug users.
They also cause urinary tract-, lower respiratory- and eye infections.
-
Diseases
-
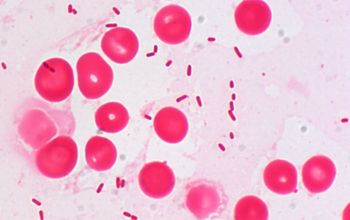
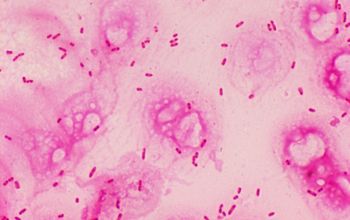
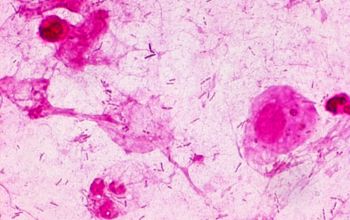
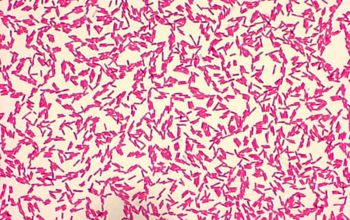
Gram stain
the following information is not yet verified
Gram-negative rods.
0.5-0.8 by 1.5-3.0 µm
they are usually thinner than Enterobacteriaceae
-
Culture characteristics
-
the following information is not yet verified
Obligate Aerobic
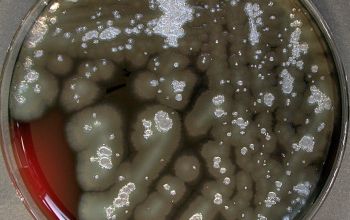
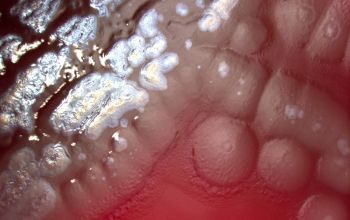
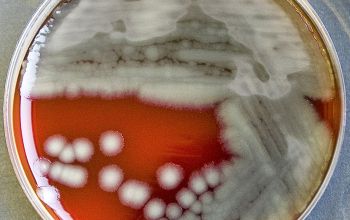
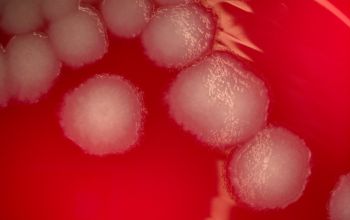
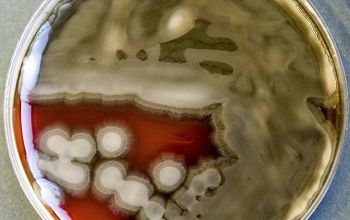
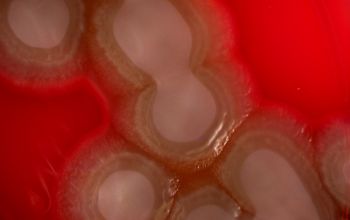
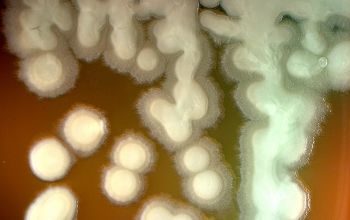
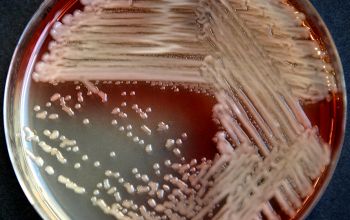
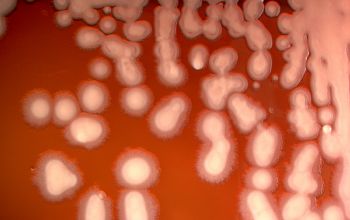
BA: 3 colony types:
1) small, rough, wrinkled
2) large, flat and spreading, serrated edge and a metallic sheen (associated with autolysis of the colony)
3) mucoid, sphere, smooth surface
Often they are ß-hemolytic.
Colonies tend to swarm.
They produce a blue-green metallic pigment (pyocyanine).
The blue-green color is a mixture of pyocyanine and pyoverdine.
Other colors pigment:
- yellow green - pyoverdine (Fluorescens group)
- reddish brown - pyorubrine
- brown black - pyomelanine
Colonies and surrounding medium have this color.
Mucoid isolates from CF(often poor prognosis) patients may undergo several phenotypic changes, including slow growth, loss of motility, and loss fof pigment production.
Some strains produce many extracellular polysaccharide slime, which grow as slimy colonies.
These are often non-pigmented colonies, and often have a slow oxidase reaction.
These are common in CF patients.
McConkey: growth, non lactose fermenter
often with blue or metallic sheen colonies
BBAØ: no growth
Odor/smell
Grape-like odor, caused by the production of pyocyanine
Bouillon
In bouillon the P.aeruginosa grows with a fleece on the surface.
Production of pyocyanin, water-soluble blue pigment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
-
the following information is not yet verified
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition