Finegoldia magna
-
General information
the following information is not yet verified
Taxonomy
Family: Peptostreptococcaceae
Formerly Peptostreptococcus magnus
Natural habitats
Gram positive anaerobic cocci are part of the normal microbiota of the mouth, upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts, female genitourinary system and skin.
Gram positive anaerobic cocci constitute 1-15% of the normal oral micobiota.
P. micros is usually considered to be the predominant species of gram-positive anaerobic cocci in the oral micribiota and
P. anaerobius and Finegoldia magna are also present in the oral cavity.
F. magna and A. prevotii are also common in the gastrointestinal tract.
F. magna is most frequently identified on the microbiota of the skin.
Clinical significance
Most infections involving anaerobic cocci ar polymicrobial.
F. magna is the most pathogenic and one of the most frequently isolated gram-positive anaerobic coccal found in human clinical specimens.
Also isolation in pure culture.
-
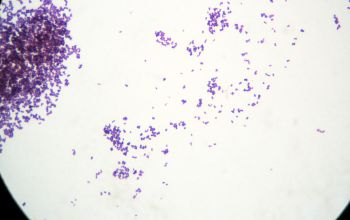
Gram stain
the following information is not yet verified
Gram positive cocci,
>0.6 µm,
lying in pairs, tetrads, or clusters
-
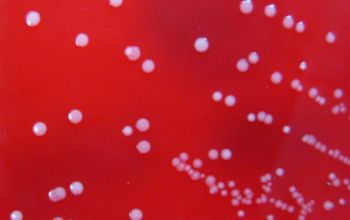
Culture characteristics
-
the following information is not yet verified
Obligate anaerobic
BBAØ: small colonies, (<1.0mm), often with variation in size and colour.
Colonies Maybe both convex and whitish and flatter and translucent on the same plate.
-
the following information is not yet verified
-
Characteristics
-
References
James Versalovic et al.(2011) Manual of Clinical Microbiology 10th Edition
Karen C. Carrol et al (2019) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th Edition